|
Capturing spatial data by laser scanning, digital photogrammetry and satellite imaging technologies, which cover object extraction from laser scanned data and high resolution satellite images, geometric corrections of aerial and satellite images, change detection based satellite and aerial photographs. Figure 32 is an example of 3D cyber-city generated from air photos, a 3-D GIS model, and data captured in the field.
Figure 32. Cyber-city model of Kowloon, Hong Kong
Selected recent publicationsZhu, C.Q., Shi, W.Z., Pesaresi, M., Liu, L.T., Chen, X.L. and King, Bruce (2005). The recognition of road network from high-resolution satellite remotely sensed data using image morphological characteristics, International Journal of Remote Sensing. Shi, W.Z. and Shaker, A. (2003). Analysis of terrain evaluation effects on IKONOS imagery rectification accuracy by using non-rigorous models, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 69(12):1359-1366. Shi, W.Z. and Zhu, C.Q. (2002). The line segment match method for extracting road network from High-Resolution satellite images. IEEE Transactions on GeoScience and Remote Sensing. 40(2):511-514. Zhu, C.Q., Shi, W.Z. and Wan, G. (2002). Reducing remote sensing image and simplifying DEM data by multi-band wavelet. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(3):525-536. Shi, W.Z. and Ehlers, M. (1996). Determining Uncertainties and Their Propagation in Classified Remote Sensed Images-Based Dynamic Change Detection. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(14):2729-2741.
Selected projects on Spatial data infrastructure for cyber-cityAdvanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology John SHI, Christopher GOLD and Geoffrey SHEA This project developed the Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology and to provide a cooperative research mechanism between The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) and local industries in the area of spatial information technology. The research target was to develop technologies for Cyber Hong Kong, which is a digital representation of Hong Kong in a computer environment (Figure 33).
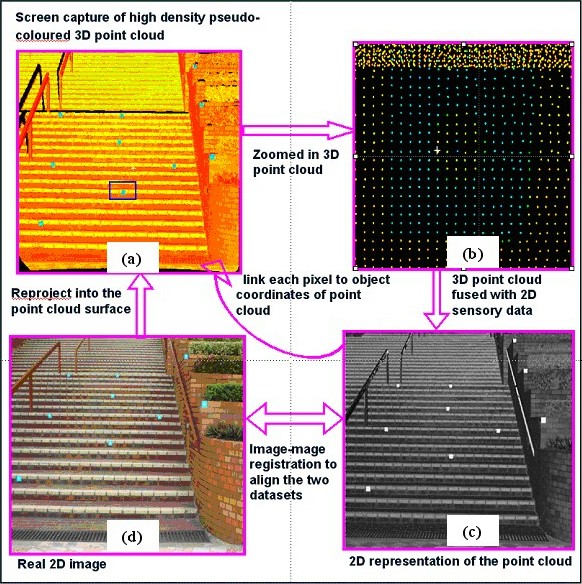
Figure 33. Integrated 3D GIS and VR for real estate planning Building Object Extraction from Laser Scanned Data John SHI, Bruce KING and Christopher GOLD One of the most critical issues for the sustainable development of spatial data infrastructure is to develop efficient data capturing approaches. This project will develop one solution to this issue. Its aim is to provide methods of recognizing building objects from high-resolution satellite images. The project will be realized by completing the following: (a) developing methods for extracting building objects based on geometric patterns and spectral attributes from high-resolution satellite images and other related information from digital maps; (b) implementing the newly proposed methods as computer software; and (c) conducting a case study in an area in Hong Kong to test the performance of the developed methods. Automatic multisensor fusion of TLS and photographic data Bruce KING and Eric Kwabena FORKUO Terrestrial laser scanners provide high density, accurate spatial data, but do not (typically) provide high quality spectral information and are earth-bound. Cameras produce high quality spectral information and can be moved freely about an object, but photogrammetrically extracting 3D data can be cumbersome and time consuming. Methodologies to exploit the positive characteristics of these two technologies to automatically produce representations that contain high quality spatial and spectral information have been developed (Figure 34).
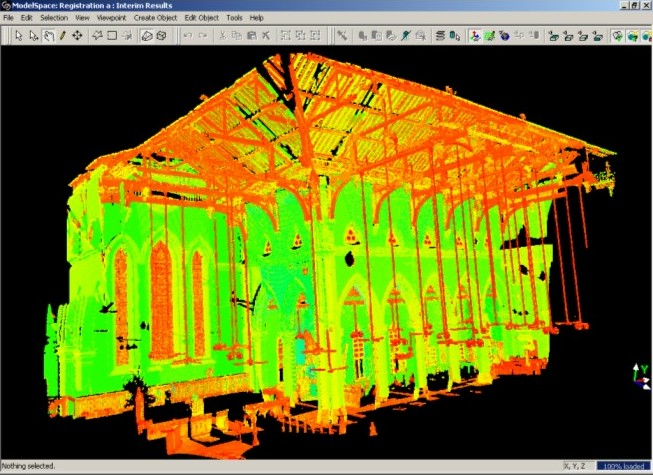
Figure 34. Multi-sensor fusion of imagery and point clouds. (a) Intensity mapped point cloud, (b) zoomed in section showing discrete points, (c) a Synthetic Camera Image, (d) real photographic image. Cultural Heritage Recording Bruce KING As an example of the application of terrestrial photogrammetry and laser scanning applied to the recording and modeling of Hong Kong’s cultural fabric, a pilot project has been completed that entailed the laser scanning of the interior and exterior of St. John’s Cathedral and its Annex, the Li Hall, for the purpose of creating architectural drawings. This project was done in conjunction with the Department of Architecture, The Chinese University of Hong Kong. Over 100 individual scans from the Department’s CYRAX 2500 laser scanner were geo-referenced into coherent point clouds to form a full 3D representation of the Cathedral and Hall (Figure 35). Sections of the point clouds were then extracted and detail drawings made from them using CAD software. At the same time a photogrammetric survey was done of the exterior of the Cathedral. The results were a set of drawings for the engineering restoration and development of the two structures and some photo textured 3D models.
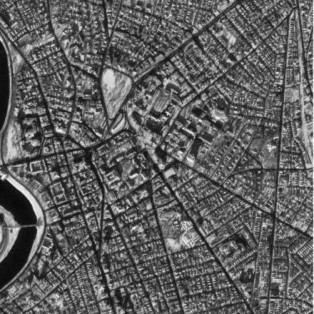
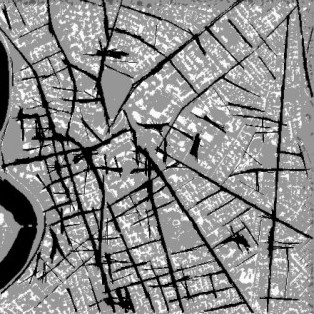
Figure 35. An interior point cloud Fusion Methods for Multi-Sensor Satellite Images John SHI, Janet NICHOL and ZHU Shu-long A one-metre panchromatic IKONOS image has a higher spatial resolution but relatively lower spectral resolution. This project develops advanced image-fusion methods to integrate one-metre panchromatic IKONOS with multi-spectral images. The result is an enhanced image with both high spatial and spectral information. Two levels of image fusion methods are developed: (a) pixel-based image fusion method and (b) feature-based image fusion method and the newly developed methods and prototype system are applied to urban environmental studies in Hong Kong. Extracting linear features from high-resolution satellite images John SHI, CHEN Yong-qi and ZHOU Cheng-hu This research project develops methods for extracting linear features, such as roads, from high resolution satellite images for GIS data updating. (Figure 36) gives an example of extracting road network from high resolution satellite images by applying the developed ‘line segment match’ algorithm from this research.
Figure 36. An example of road network extraction from high resolution IKONOS satellite images. (a) the original image, (b) processed image, (c) the extracted road network, and (d) overlapped road network overlaid on the original for comparison purposes. |