-
Background
Building and civil engineering works have been playing a significant role in the infrastructure development of Hong Kong. Recent construction works such as Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge, West Kowloon Cultural District, a new development in Kai Tak areas and other forthcoming construction works are anticipated to reach 160 billion in the next 10 years. With such huge construction demands involving different levels of personnel from workers to project managers on-site, the safety and health issues in construction sites are of great concern. Construction workers are often exposed to physical environmental hazards on-site, such as heat, UV radiation, noise and air pollution. Excessive exposures to these hazards may result in injury, chronic illness, permanent disability or even death. For example, prolonged work under the direct sun may cause sunburn, heat exhaustion, or even heat stroke. Several cases of heat stroke have been reported from the construction industry in the last few years. High decibel levels from operating machines may also distract concentration and even cause permanent hearing loss under long period exposures. Dust pollution in construction sites is a common and well-recognized problem, long-term exposure to excessive dust may cause serious lung diseases.
A good practice of safety and health management not only protects construction workers from environmental-related hazards, the improved working environment can also escalate working efficiency and productivity, thus creating a win-win situation. In current practices, safety officers report and announce weather and environmental indices such as temperature and air quality health index based on the information from the Hong Kong Observatory (HKO) and Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department (HKEPD). However, data provided by HKO and HKEPD are collected at limited locations, representing only at district-scale. This information is not accurately representing the rapidly changing and adverse micro-environmental conditions in construction sites. Thus, a real-time, automatic and Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring System (IEMS) can significantly facilitate safety and health assessment. A bespoke mobile micro-environmental sensing device has been successfully developed by our research team to provide a low cost, a well-established automatic environmental quality monitoring solution in construction sites.
-
Research Aim and Objectives
- Enhancement of Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring Systemg
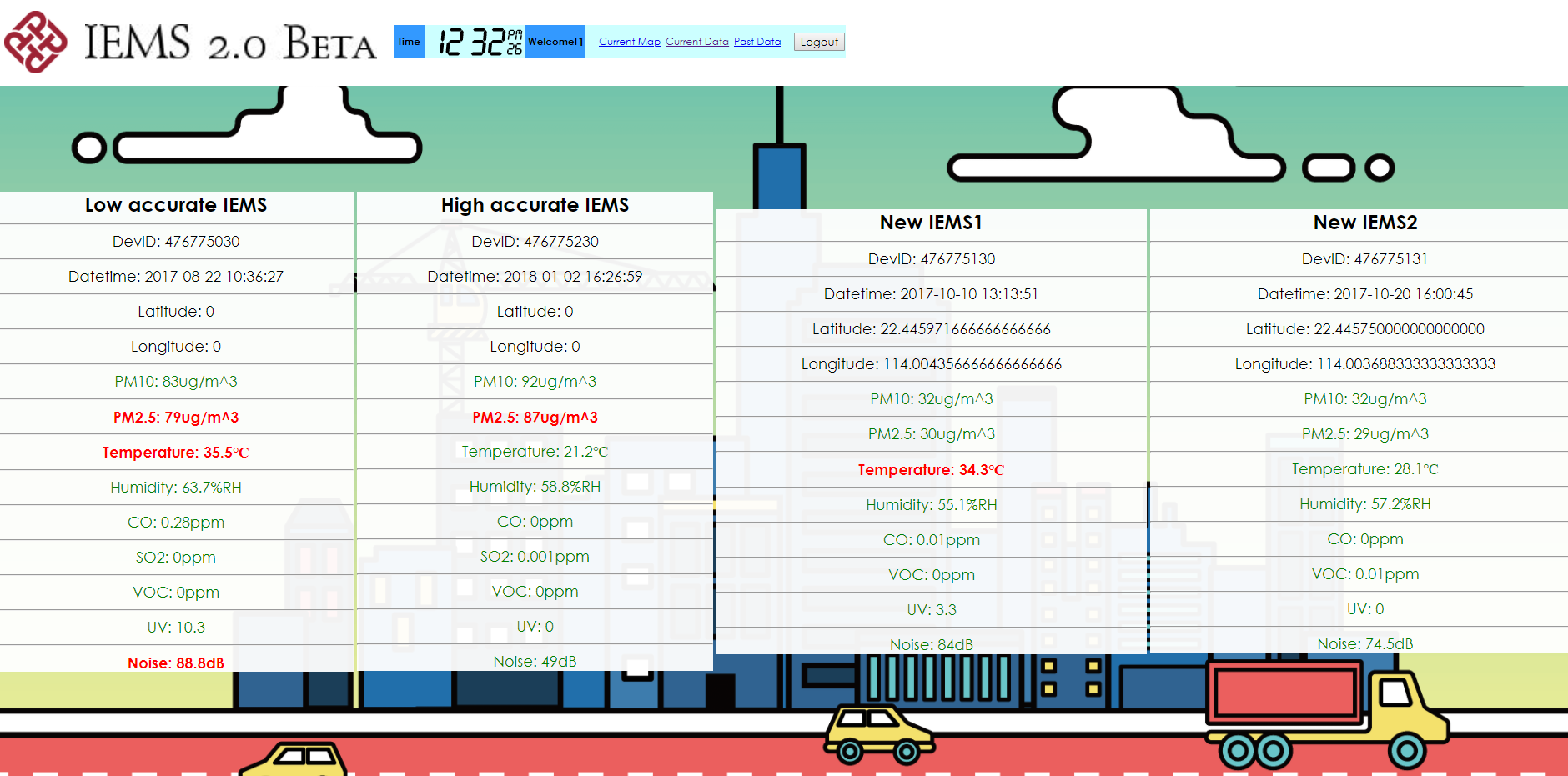
The developed Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring System (IEMS) is equipped with a microcontroller, wireless communication modules, and environmental sensors including temperature, humidity, UV radiation, noise level, and dust intensity sensors. This system can further be enhanced to incorporate GPS modules, and advanced sensors for detecting micro-environmental quality on-site, with reasonable accuracy of both indoor and outdoor positioning and environmental conditions. The system can be installed anywhere on-site and can be carried by safety officers to collect environmental-related data. - Enhancement of micro-environmental quality monitoring on-site
The system is used to provide an automatic risk assessment. Continuous environmental data is collected from mobile devices and analysed in web server. Environmental indices are generated from our system, which can be accessed by the safety officers and site managers through their smartphones to provide “warning” services. Safety officers and site managers can evaluate the micro-environmental conditions on-site in order to enforce appropriate preventive measures. - Analysis tool for environmental impact assessment during construction process
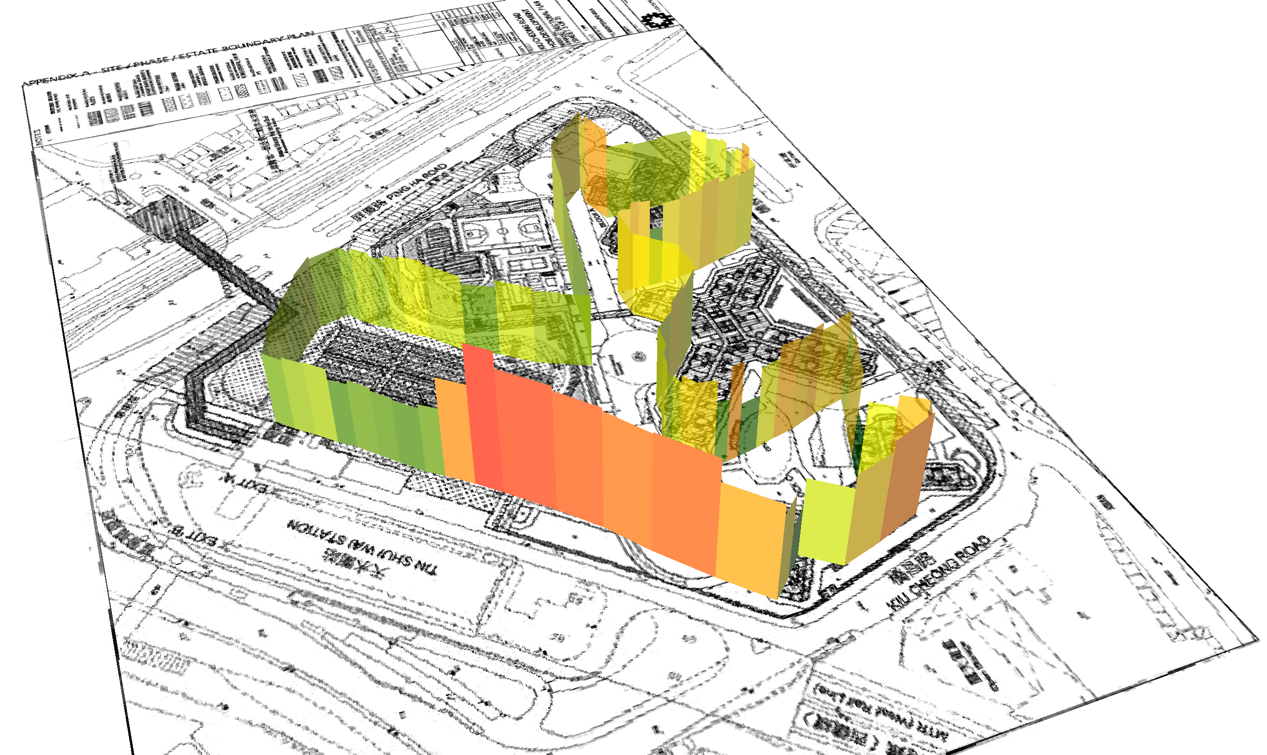
Effective construction practices can help to control and reduce environmental pollution. The system is used as an analysis tool to evaluate each environmental factor during the construction process, at three construction sites. - Raise the awareness of environmental quality in working environment
The real-time generated environmental indices and “warning” notices can convey clear messages to construction workers to take corresponding protective measures. Analysis results and findings from this project are disseminated in order to promote the awareness of the working environment. - An updated Alert and Warning System
A modified alert system with three warning signals (Good, Unhealthy and Hazardous) and the corresponding warning messages are devised.
The objective of this project is to deploy a low cost, extendable, and automated micro-environmental monitoring system in construction sites. Listed below are the specific objectives of this development:
- Enhancement of Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring Systemg
-
Project Significance
This study demonstrates an effective system to monitor construction sites’ environment with the help of the IEMS and a robust alert and warning system. In case of fair environmental conditions in construction sites, this system can assist operational management at the construction sites such as water spraying facilities near site entrances when the PM2.5/PM10 concentrations exceed the threshold. In addition, this system can be used as an innovative technology for monitoring the environmental conditions under the framework of Smart City, while a set of time-series data under various conditions is necessary for the future work. In the future, the IEMS can be integrated with BIM of the constructions sites. Data collected from IEMD and BIM-based microclimate simulation can be useful to monitor and provide guidelines related to the environmental conditions during the construction progress.
-
Acknowledgement
This research project “A practical application of Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring System for construction sites” (Project Number: CICR/08/14) is funded by the Construction Industry Council Fund.
A Practical Application of Integrated Micro-Environmental Monitoring System for Construction Sites
Construction workers are exposed to a wide variety of hazards on-site, for example, heat, noise, UV radiation and dust. Excessive exposures to these hazards may result in injury, chronic illness, or even death. Thus, safety and health management are indispensable in construction projects. In current practices, safety officers report and announce current weather and environmental indices such as temperatures and air quality health index. However, locational-based information from the Hong Kong Observatory and the Environmental Protection Department may not be able to reflect the changing environmental conditions on-site accurately. Thus, a real-time, automated, and Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring System (IEMS) can significantly facilitate the health risk/hazard screening in construction sites. Our research team has designed a low cost Integrated micro-Environmental Monitoring Device (IEMD) for monitoring localised environmental conditions which are further enhanced for real-time environmental monitoring in construction sites. Different sensors for environmental monitoring (e.g. temperature, humidity, UV radiation, noise level, and dust intensity), positioning (GPS), communication (3G/4G networking) and visualization (web interface and Android App) are embedded along with a service platform to prevent possible environmental hazards.
In addition, a progressive approach is adopted to devise a robust alarm and warning system. In this study, the project team integrates the classification of parameters and corresponding health risk into three generalized categories, keeping in view air quality objectives of HKEPD and USEPA. Our designed alarm/warning system is a simple and convenient system for the construction workers. Each category of this system indicates a working condition: “Good” class indicates an overall acceptable condition of work; “Unhealthy” class describes a situation where workers with health risks should reduce workload and others can continue working after taking precautionary measures, and “Hazardous” class indicates a critical situation in which workers with health risk should stop working while healthy workers should reduce prolonged exposure in the affected sites. This alert and warning system is integrated with mobile application and it will generate a warning notification if any of the environmental parameters exceed the defined thresholds.
Safety officers and site managers evaluate the environmental conditions on-site, so that appropriate preventive measures can be enforced. The system also provides an analysis tool for environmental impact assessment during various stages of the construction process. This project is to (i) provide an effective service platform for environmental monitoring in construction sites, with the ability to incorporate real-time environmental information (ii) enhance the current risk assessment on-site; and (iii) raise the awareness of environmental quality in the working environment. This system can also be modified for other applications (e.g. in bus terminal, shopping mall, factory, as well as in household apartment).