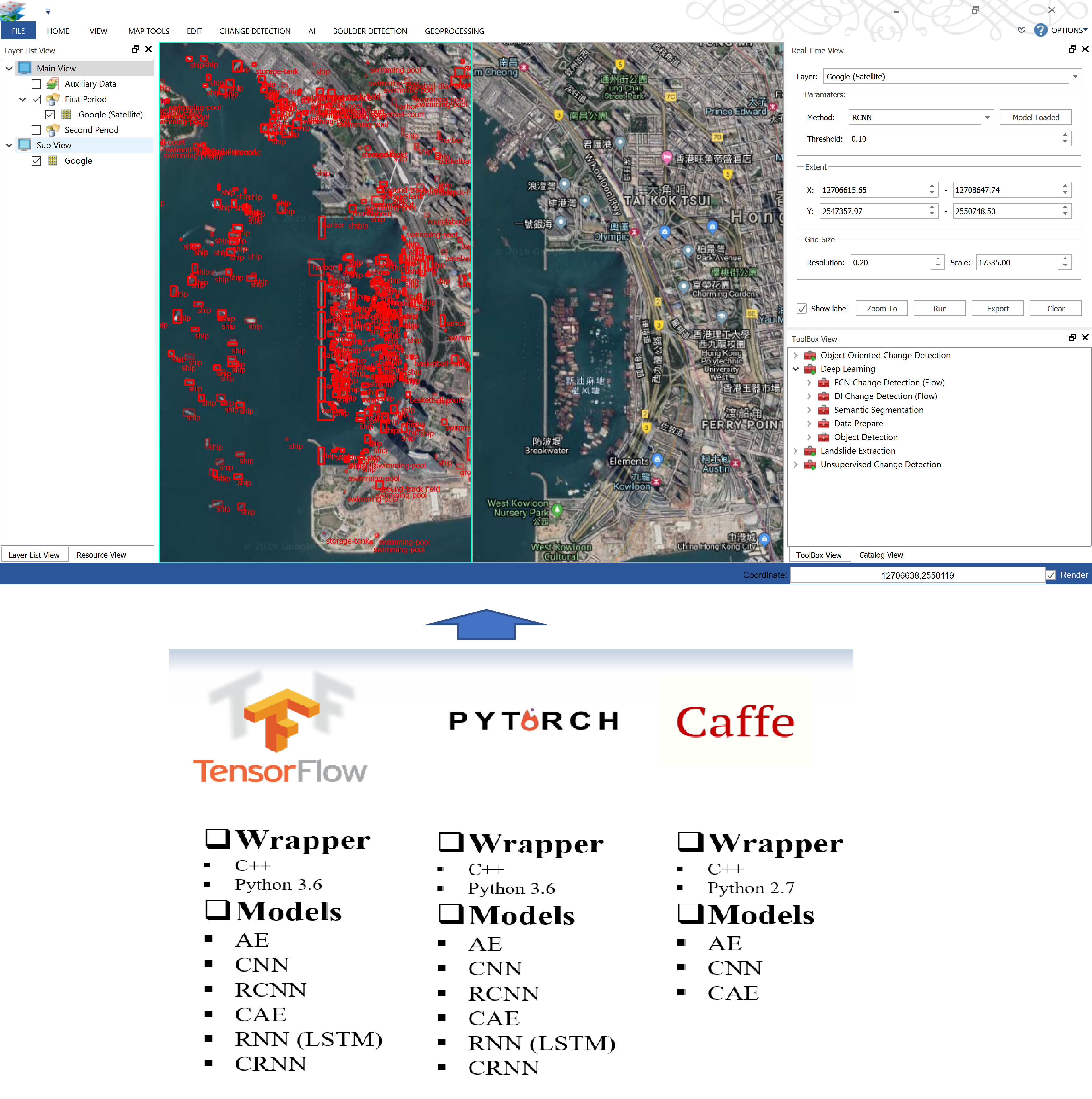
智慧城市與空間大數據分析實驗室
AI城市目標監測
AI(人工智能,也稱機器智能)受生物系統啟發,能夠正確解釋外部資料,從資料中學習知識並通過靈活的適應來實現特定目標和任務。我們的AI技術研究內容包括最新出現的深度學習方法、新型網路結構、智能的機器學習算法和AI技術在城市目標監測中的應用,並研發集成多種深度學習框架和模型的圖像分析軟體(ImageAnalytics)。
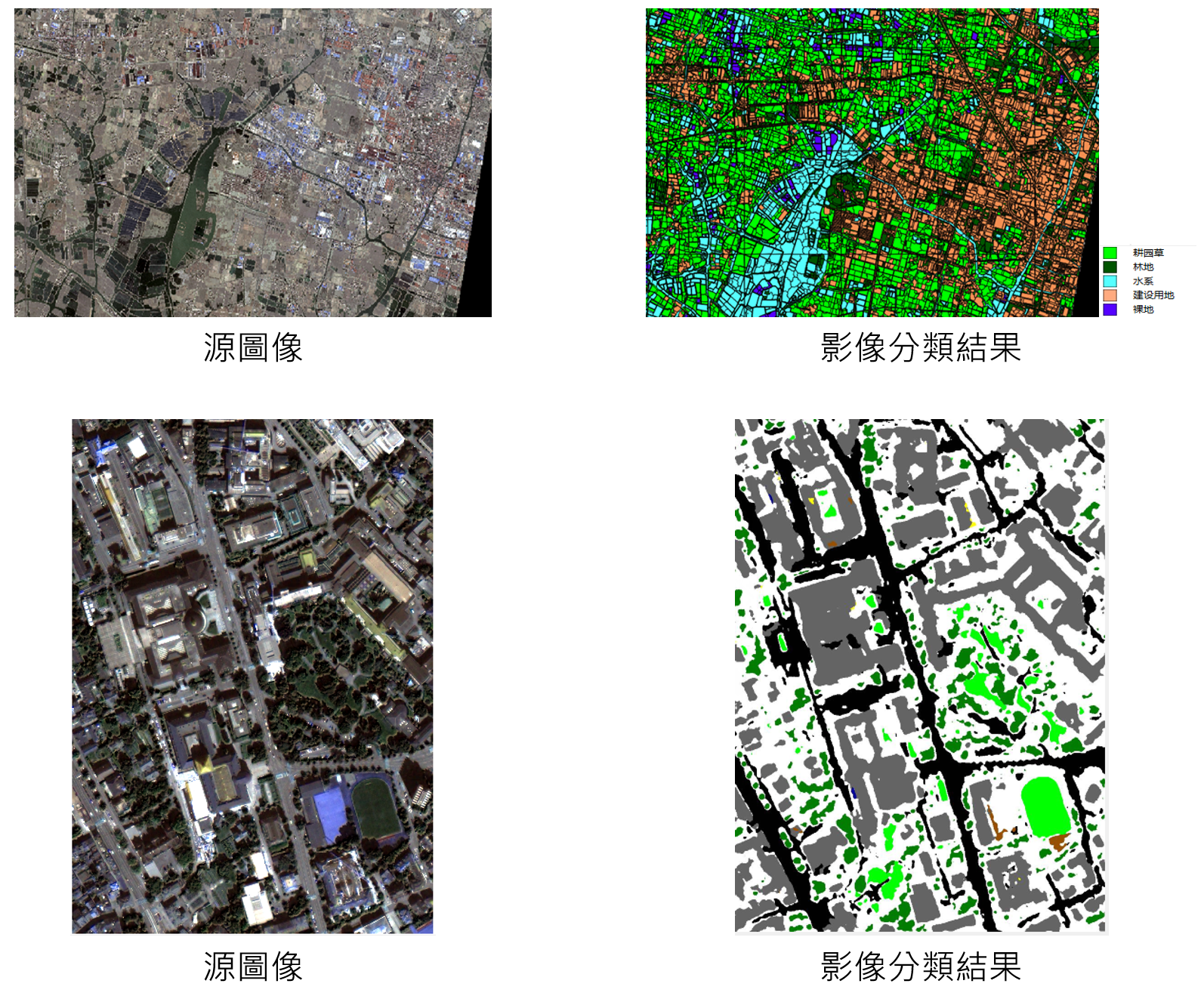
遙感影像分類
遙感影像分類技術是指對遙感影像中各類地物的光譜信息和空間信息進行特徵分析,利用不同的規則劃分不同的類別從而獲得遙感圖像與實際地物對應信息的過程。即時準確高效的影像分類算法對於國家測繪部門進行國土資源調查,開展常態化土地利用監測評估有著重要意義。近年來,隨著AI技術的發展迅速,尤其是深度學習技術的出現,為遙感影像分類方法的應用提供了強有力的支援。我們的圖像分析軟體實現了多種遙感影像分類技術工具,包括一系列基於機器學習的面向對象遙感影像分類以及最新的基於深度學習的遙感影像分類方法。

遙感目標提取
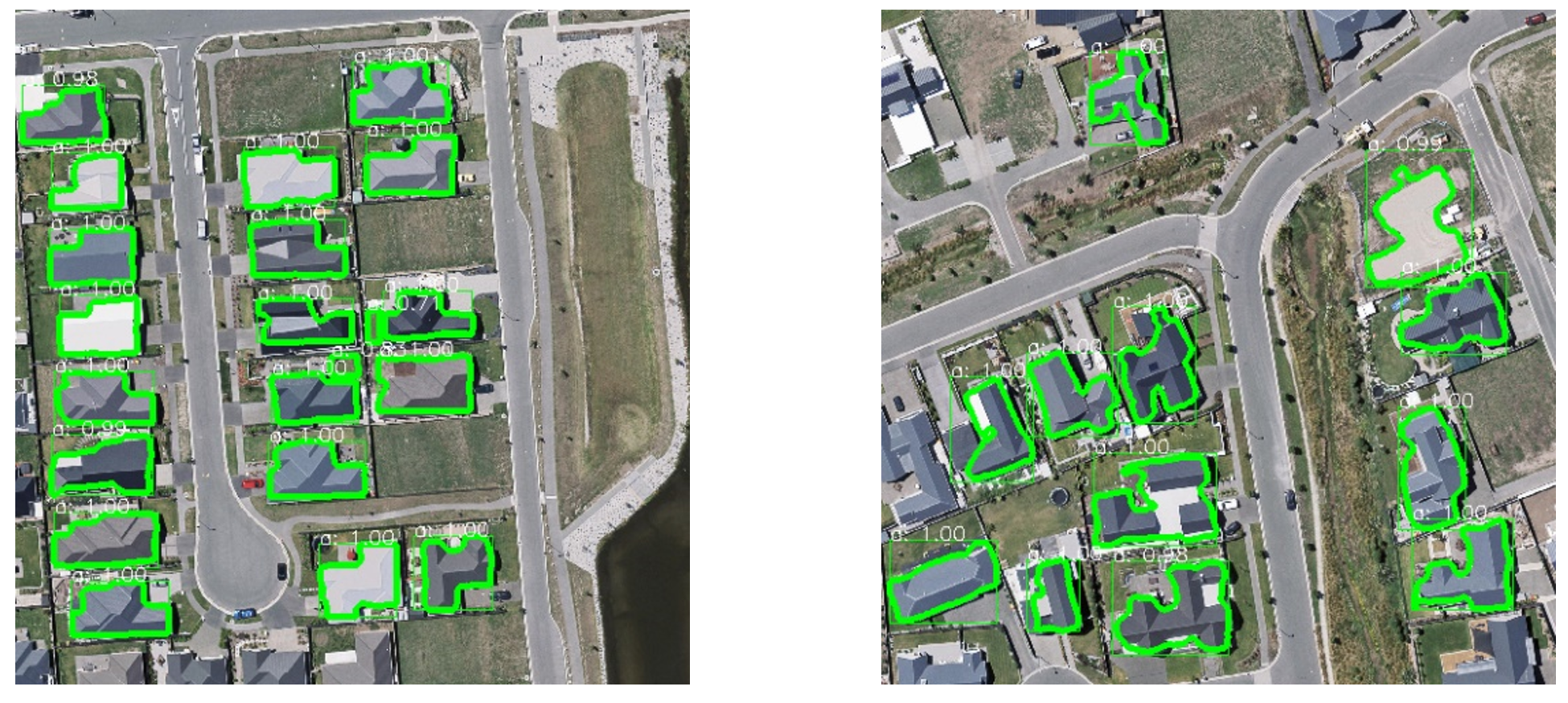
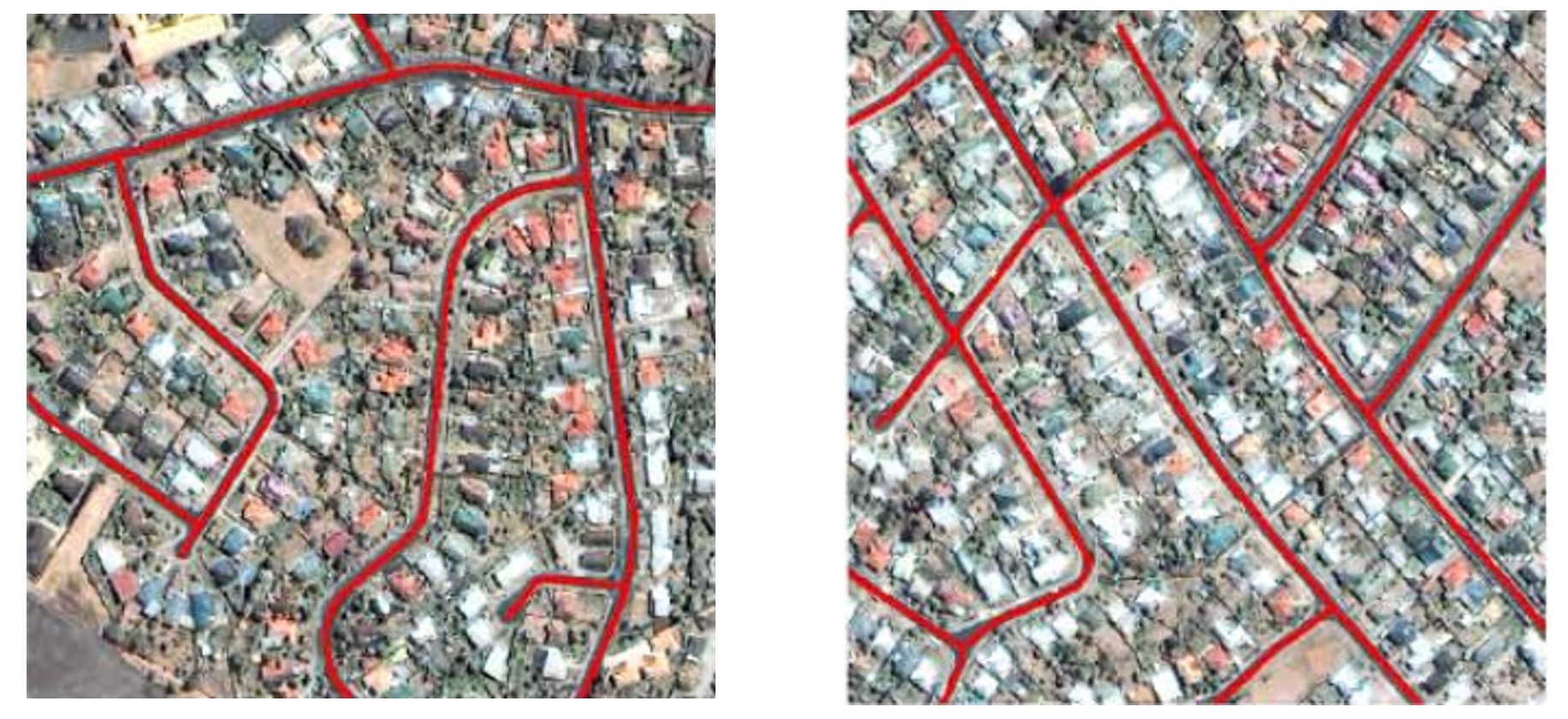
我們研究的遙感目標提取主要是關注人造地物的提取,例如建築物提取和道路提取。建築物由於形狀變化大,周圍環境複雜性,其檢測具有挑戰性。機載LiDAR具有高程信息,可以有效區分地麵點和非地麵點,提高了建築物檢測的自動化程度,但平面精度不高,與樹的區分也是難點;高解析度影像具有豐富的光譜、紋理和幾何信息,能夠提供精細的邊界,但同時帶來光譜模糊性,遮擋,陰影等。從它們的特性可以看出,LiDAR和影像天然互補,因此結合LiDAR和影像進行自動建築物檢測。我們提出一種通過LiDAR資料和高空間解析度影像融合的自適應迭代分割自動建築物提取算法。該算法不需要樣本,不設置特定閾值,不依賴分割參數的設置,在ISPRS Vaihingen數據集上的測試精度達到85.5%。

傳統的遙感影像建築物信息檢測,大部分通過手工設計特徵來充分利用影像信息,利用聚類、分割、邊緣檢測、機器學習等方法來實現對目標地物的提取,但由於實際情況異常複雜,這些方法在運用過程中遇到很多難以克服的困難。針對這些存在的問題,我們引入AI技術,通過深度學習模型自動、準確地提取遙感影像中的建築物區域。

相關研究发表
- [1] Chen, S., Shi, W., Zhou, M., Zhang, M. & Chen, P. (2020). Automatic Building Extraction via Adaptive Iterative Segmentation With LiDAR Data and High Spatial Resolution Imagery Fusion. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 13, 2081-2095.
- [2] Miao, Z., Gao, L., He, Y.*, Wu, L., Shi, W., Samat, A., Liu, S. and Li, J. (2019) Use of colour transformation and the geodesic method for road centreline extraction from VHR satellite images, International Journal of Remote Sensing. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1558374.
- [3] Gao, L., Shi, W.*, Miao, Z. and Lv, Z. (2018) Method based on edge constraint and fast marching for road centerline extraction from very high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sensing, 10(6), Article number 900 DOI: 10.3390/rs10060900.
- [4] Li, Z., and Shi, W.* (2016). Partial differential equation-based object extraction from remote sensing imagery, Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 35(3), 257-262. DOI: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.03.001.
- [5] Miao, Z., Shi, W.*, Samat, A., and Lisini, G., and Gamba, P. (2016). Information Fusion for Urban Road Extraction From VHR Optical Satellite Images, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 9(5), 1817-1829. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2498663.
- [6] Miao, Z., Shi, W.*, Gamba, P., & Li, Z. (2015) An Object-Based Method for Road Network Extraction in VHR Satellite Images, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 8(10), 4853-4862. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2443552.
- [7] Li, Z., Shi, W.*, Wang, Q., & Miao, Z. (2015). Extracting man-made objects from high spatial resolution remote sensing images via fast level set evolutions, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 53(2), 883–899. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2330341.
- [8] Miao, Z., Wang, B., Shi, W.*, Wu, H., & Wan, Y. (2015). Use of GMM and SCMS for automatic extraction of road centerline from the classified image, Journal of Sensors, vol. 2015, Article ID 784504. DOI: 10.1155/2015/784504.
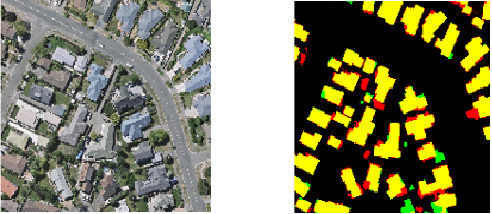
滑坡製圖
滑坡是世界上最嚴重的自然災害之一,滑坡災害造成的人員傷亡以及經濟和環境破壞日益嚴重。區域性滑坡製圖目前主要通過遙感目視解譯來開展,存在主觀性強、耗時費力、提取精度低等問題,導致難以滿足災後應急調查、災情評估等方面的應用需求。借助AI在遙感影像處理中的強大分析、表達能力,我們採用基於卷積神經網絡的多時相光學遙感影像滑坡檢測方法,結合數字高程模型DEM提供的地形信息,能夠有效識別滑坡的位置、範圍、軌跡、高程等信息,從而實現滑坡空間分佈及其屬性信息的準確識別,為災後應急調查提供技術支撐。

相關研究發表
- [1] Shi, W., Zhang, M., Ke, H., Fang, X., Zhan, Z. & Chen, S. (2020). Landslide recognition by deep convolutional neural network and change detection. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS. 2020.3015826.
- [2] Zhang, M., Shi, W., Chen, S., Zhan, Z. & Shi, Z. (2020). Deep multiple instance learning for landslide mapping. IEEE Geoscience Remote Sensing Letter. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3007183.
- [3] Shi, W., Deng, S., * and Xu, W. (2018) Extraction of multiscale landslide morphological features based on local Gi* using airborne LiDAR-derived DEM, Geomorphology, 303, 229-242. DOI:10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.12.005.
- [4] Lv, Z.*, Shi, W.*, Zhang, X., and Benediktsson, J. (2018) Landslide Inventory Mapping From Bitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Using Change Detection and Multiscale Segmentation, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(5), 1520. (IF=2.913) DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2803784.
- [5] Li, Z.*, Shi, W.*, Myint, S.W., Lu, P., & Wang, Q. (2016). Semi-automated landslide inventory mapping from bitemporal aerial photographs using change detection and level set method, Remote Sensing of Environment, 175, 215-230. DOI:10.1016/j.rse.2016.01.003.
- [6] Li, Z.*, Shi, W., Lu, P., Yan, L., Wang, Q. and Miao, Z. (2016). Landslide mapping from aerial photographs using change detection-based Markov random field, Remote Sensing of Environment, 187, 76-90.
- [7] Deng, S.*, & Shi, W. (2014). Semi-automatic approach for identifying locations of shallow debris slides/flows based on lidar-derived morphological features. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(10), 3741-3763. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2014.915438.
遙感變化檢測
遙感影像能夠直接或間接的反應地表覆蓋和土地利用信息,是用來獲取地球表面變化信息的重要手段。利用遙感影像進行變化檢測,在地表覆蓋和土地利用、地質災害、城市變化、環境、濕地、農業、林業等領域都有重要應用。深度學習技術作為新興的智能化數據處理化技術,能夠從多時相海量遙感資料中快速、精確的發現變化,已經成為我們一個重要的研究方向。基於深度學習的變化檢測軟體工具可以從多時相遙感影像中快速提取變化信息,為智慧城市的目標監測和資料更新提供技術支援。
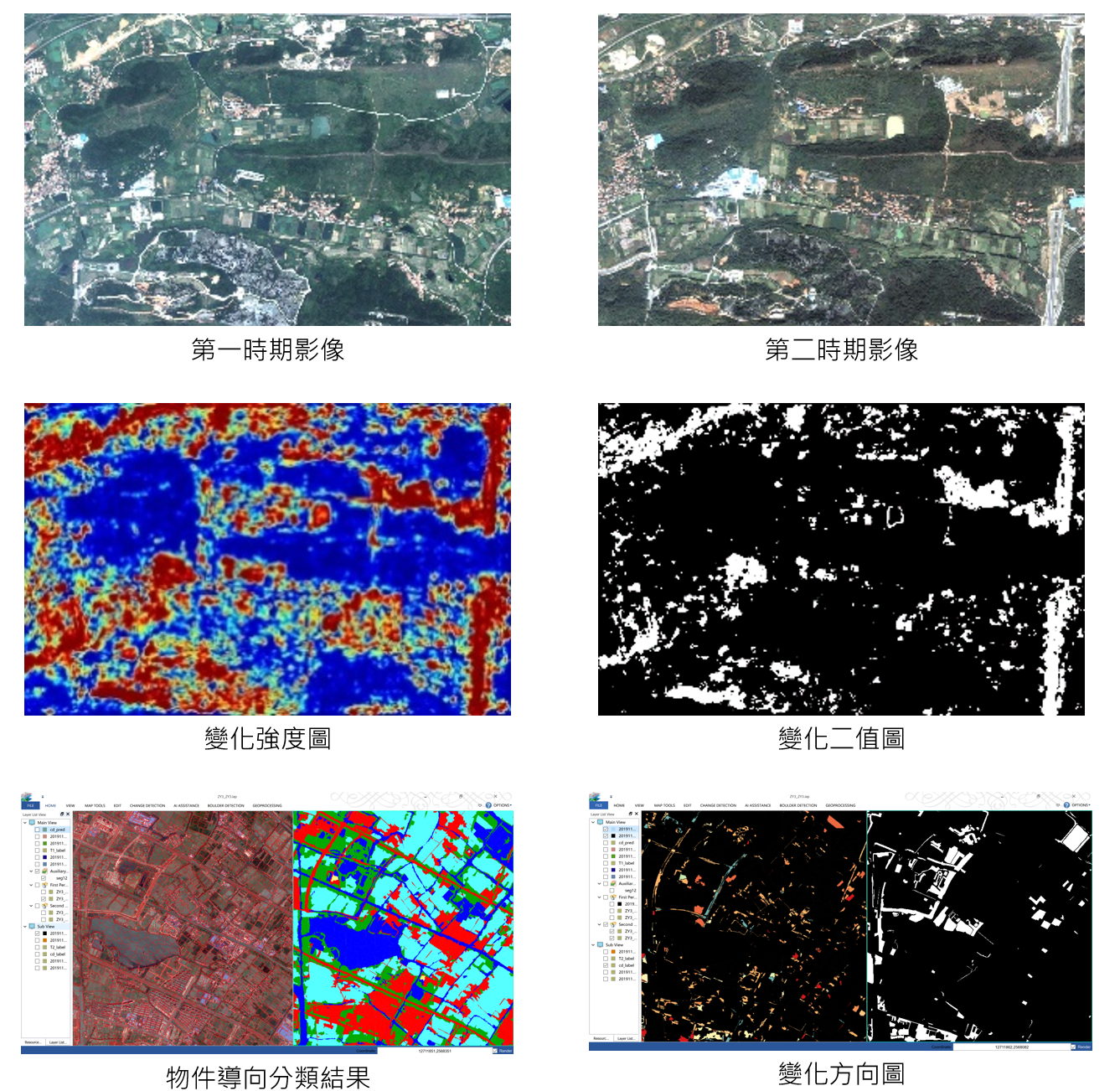
相關研究發表
- [1] Shi, W., Zhang, M., Zhang, R., Chen, S. & Zhan, Z. (2020). Change detection based on artificial intelligence: state-of-the-art and challenges. Remote Sensing, 12(10), pp. 1688.
- [2] Zhang, M. & Shi, W. (2020). A feature difference convolutional neural network-based change detection method. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2981051.
- [3] Zhang X, Shi W.*, Lv Z, et al. (2019). Land Cover Change Detection from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using Multitemporal Deep Feature Collaborative Learning and a Semi-supervised Chan–Vese Model. Remote Sensing, 11(23): 2787.
- [4] Choudhary, K.*, Shi, W., Boori, M-S. and Corgne, S. (2019) Agriculture Phenology Monitoring Using NDVI Time Series Based on Remote Sensing Satellites: A Case Study of Guangdong, China, Optical Memory and Neural Networks, 28(3), 204–214. DOI: 10.3103/S1060992X19030093.
- [5] Hasan, S., Shi, W.*, Zhu, X. and Abbas S. (2019) Monitoring of Land Use/Land Cover and Socioeconomic Changes in South China over the Last Three Decades Using Landsat and Nighttime Light Data, Remote Sensing, 11(14), 1658. DOI: 10.3390/rs11141658.
- [6] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Ye, Y., Zhang, H., and Deng, K. (2019) A novel change detection approach for VHR remote sensing images by integrating multi-scale features, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(13), 4910-4933 DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1577576.
- [7] Shao, P., Shi, W.*, and Hao, M. (2018) Indicator-Kriging-Integrated Evidence Theory for Unsupervised Change Detection in Remotely Sensed Imagery, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(12), 4649-4663 DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2878759.
- [8] Cai, L., Shi, W.*, Hao, M., Zhang, H. and Gao, L. (2018) A Multi-Feature Fusion-Based Change Detection Method for Remote Sensing Images, Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 46(12), 2015-2022 DOI: 10.1007/s12524-018-0864-1.
- [9] He, P., Shi, W.*, and Zhang, H. (2018) Adaptive superpixel based Markov random field model for unsupervised change detection using remotely sensed images, Remote Sensing Letters, 9(8), 724-732. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2018.1470698.
- [10] Lv, Z.*, Shi, W.*, Benediktsson, J., and Zhou, X. (2017) Semi-Automatic System for Land Cover Change Detection Using Bi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 9(11), 1112.
- [11] Li Z.*, Shi W., Zhang H.*, and Hao M. (2017). Change Detection Based on Gabor Wavelet Features for Very High Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 14(5): 783-787.
- [12] Zhang, X., Shi, W.*, Liang, P., and Hao, M. (2017) Level Set Evolution with Local Uncertainty Constraints for Unsupervised Change Detection, Remote Sensing Letters, 8(8), 811-20.
- [13] Zhang, X., Shi, W.*, Hao, M., Shao, P., and Lyu, X. (2017) Level set incorporated with an improved MRF model for unsupervised change detection for satellite images, European Journal of Remote Sensing, 50(1), 202-10.
- [14] Cai, L., Shi, W.*, Zhang, H., and Hao, M. (2016). Object-oriented change detection method based on adaptive multi-method combination for remote-sensing images, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 37(22): 5457-5471.
- [15] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Zhang, H., Wang, Q., and Deng, K. (2016). A Scale-Driven Change Detection Method Incorporating Uncertainty Analysis for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 745, DOI: 10.3390/rs8090745.
- [16] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Deng, K., and Feng, Q. (2016). Superpixel-based active contour model for unsupervised change detection from satellite images, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 37(18), 4276-4295. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2016.1210838.
- [17] Shao, P., Shi, W.*, He, P., Hao, M., and Zhang, X. (2016). Novel Approach to Unsupervised Change Detection Based on a Robust Semi-Supervised FCM Clustering Algorithm, Remote Sensing, 8(3), DOI: 10.3390/rs8030264.
- [18] Shi, W., Shao, P.*, Hao, M., He, P., and Wang, J. (2016). Fuzzy topology-based method for unsupervised change detection, Remote Sensing Letters, 7(1), 81-90. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2015.1109155.
- [19] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Deng, K., Zhang, H., and He, P. (2016). An Object-Based Change Detection Approach Using Uncertainty Analysis for VHR Images, Journal of Sensors, vol. 2016, Article ID 9078364, 17 pages. DOI: 10.1155/2016/9078364.
- [20] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Deng, K., & Zhang, H. (2015). Fusion-based approach to change detection to reduce the effect of the trade-off parameter in the active contour model, Remote Sensing Letters, 6(1), 39-48. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.1001078.
- [21] Wang, Q., Atkinson, P. M., & Shi, W.* (2015). Fast subpixel mapping algorithms for subpixel resolution change detection, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 53(4), 1692–1706. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346535.
- [22] Wang, Q., Shi, W.*, Atkinson, P. M., & Li, Z. (2015). Land cover change detection at subpixel resolution with a Hopfield neural network, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 8(3), 1339- 1352. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2355832.
- [23] He, P., Shi, W.*, Miao, Z., Zhang, H., & Cai, L. (2015). Advanced Markov random field model based on local uncertainty for unsupervised change detection, Remote Sensing Letters, 6(9), 667-676. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2015.1054045.
- [24] Hao, M., Shi, W.*, Deng, K., & Zhang, H. (2014). A contrast-sensitive Potts model custom-designed for change detection, European Journal of Remote Sensing, 47, 643-654. DOI: 10.5721/EuJRS20144736.
- [25] He, P., Shi, W.*, Hua, Z., & Hao, M. (2014). A novel dynamic threshold method for unsupervised change detection from remotely sensed images, Remote Sensing Letters, 5(4), 396-403. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.912766.
目標檢測和跟蹤
目標檢測和跟蹤是遙感影像處理乃至計算機視覺最熱門的方向之一,廣泛應用於遙感影像處理、機器人導航、工業檢測、航空航天等領域,通過計算機視覺減少對人力資本的消耗,具有重要的現實意義。因此,目標檢測和跟蹤也就成為了近年來理論和應用的研究熱點,它是影像處理和計算機視覺學科的重要分支,同時也是泛身份識別領域的一個基礎性的算法。我們將SSD、Faster RCNN、YOLO2/3等幾大流行的深度學習目標檢測和跟蹤算法集成進入了我們的圖像分析軟體,並採集資料進行訓練,可以對無人機遙感影像等資料針對任意感興趣目標進行檢測和跟蹤。軟體系統具備對遙感影像特定目標的檢測和跟蹤能力,為城市目標的快速監測提供了實用的工具。
此外,人物檢測一直是計算機視覺領域一個研究熱點,在公共安全、自動駕駛、災後救援等領域都有著廣泛的應用。目前人物檢測研究主要基於可見光影像,對於熱紅外影像人物檢測研究較少。與可見光影像相比,熱紅外影像有著無可比擬的優勢,比如環境適應性強、更好保護私人隱私等。我們將深度學習檢測算法Faster RCNN與更為先進的深度卷積網絡Inception V2,Resnet 50和Resnet 101分別結合起來,提出基於熱紅外影像的人物檢測方法,並標注資料集OTCBVS benchmark dataset進行模型訓練。實驗結果表明,這些模型檢測準確率維持在90%左右。為基於熱紅外影像採集人流信息提供了一個有效的方法。

相關研究發表
- [1] Wang, S. (2020). Human detection from thermal images by deep learning based on improved faster R-CNN. Thesis (Msc). The Hong Kong Polytechnic University.