
Dust Observation Technologies |
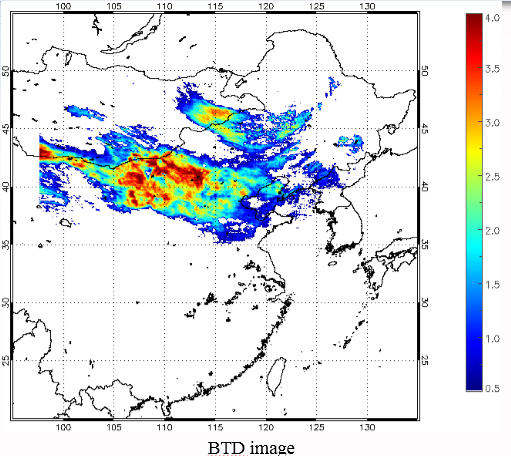
BTD (11-12 µm) can be applied to distinguish dust aerosols from clouds, since dust particles absorb more infrared radiation at shorter wavelength while ice or liquid water particles exhibit higher absorption in longer wavelengths (Prata, 1989; Ackerman 1997; Zhao et al., 2010).
 |
 |
| BTD Image | 2009/04/22-2009/04/25 |
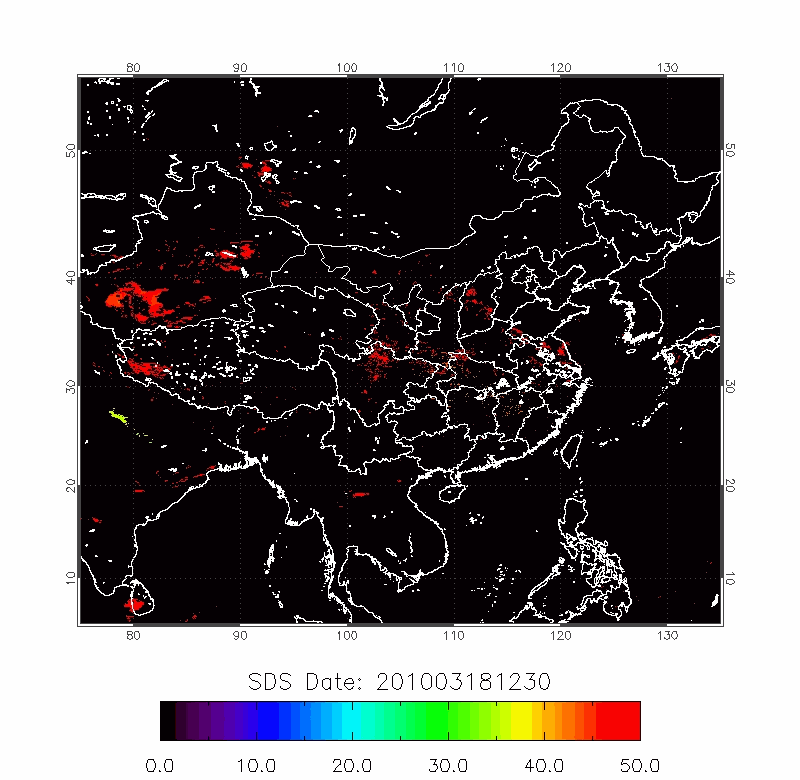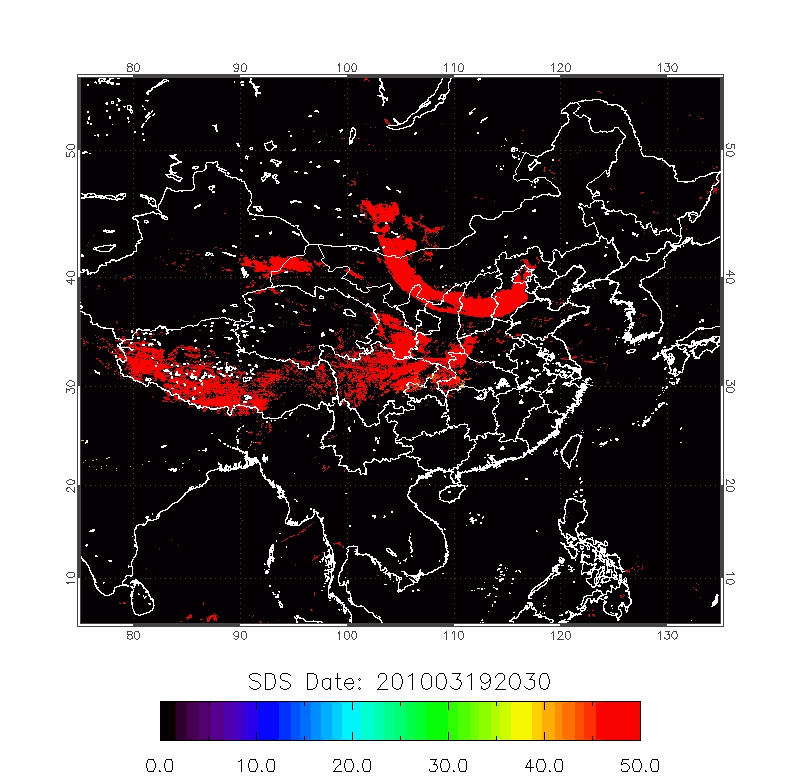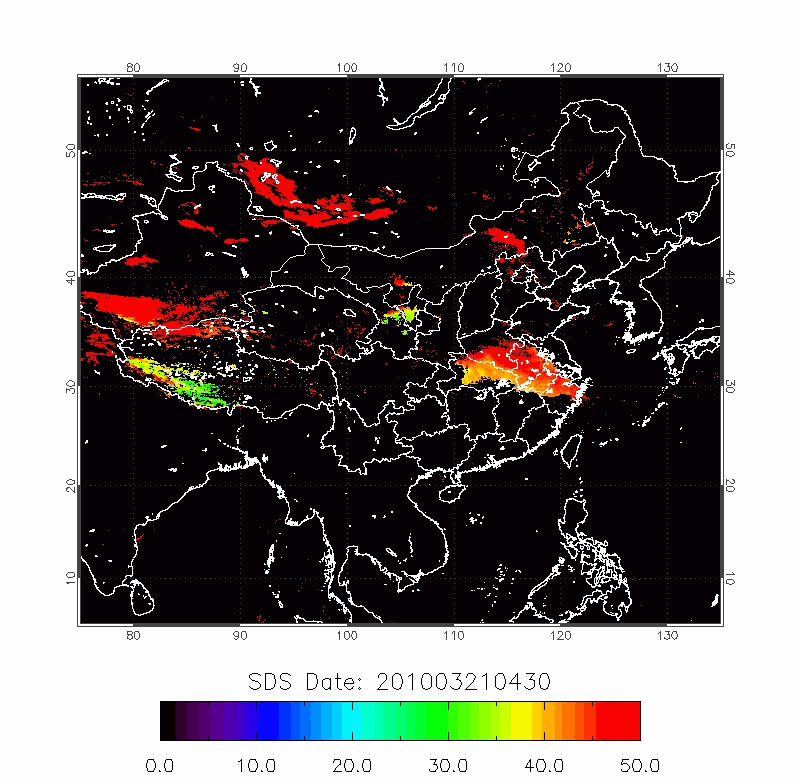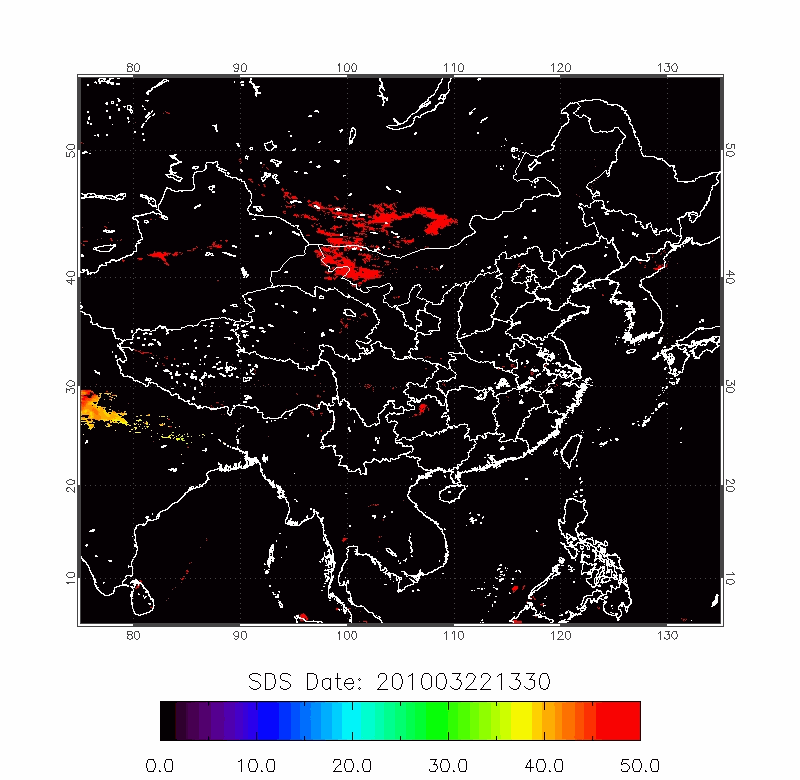 |
 |
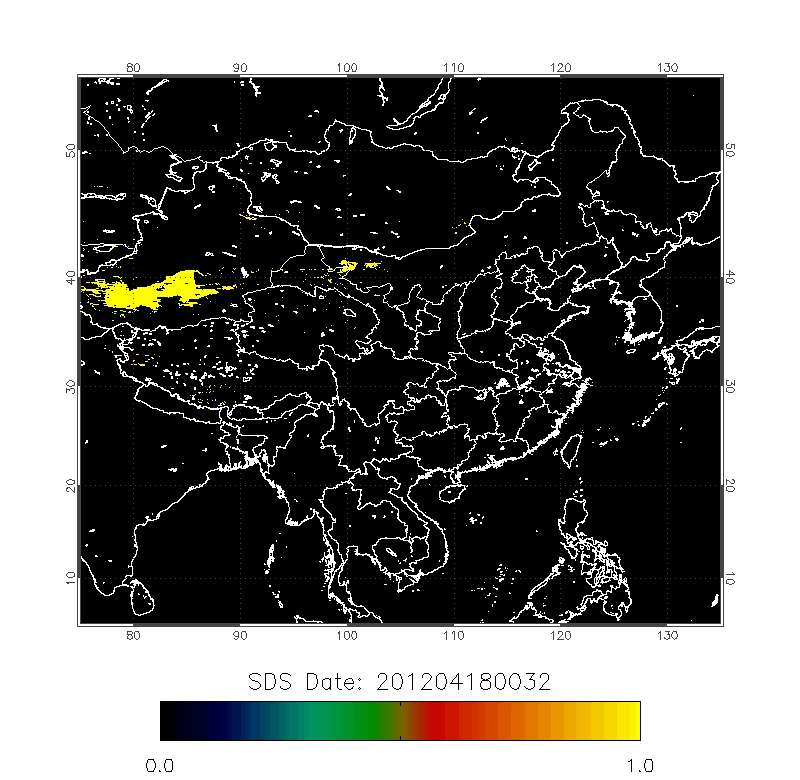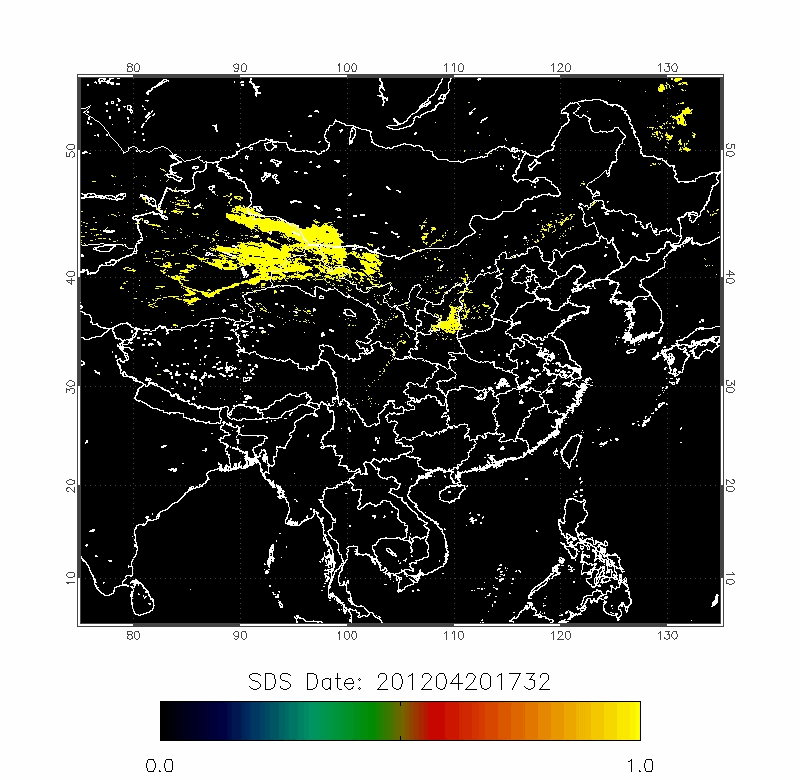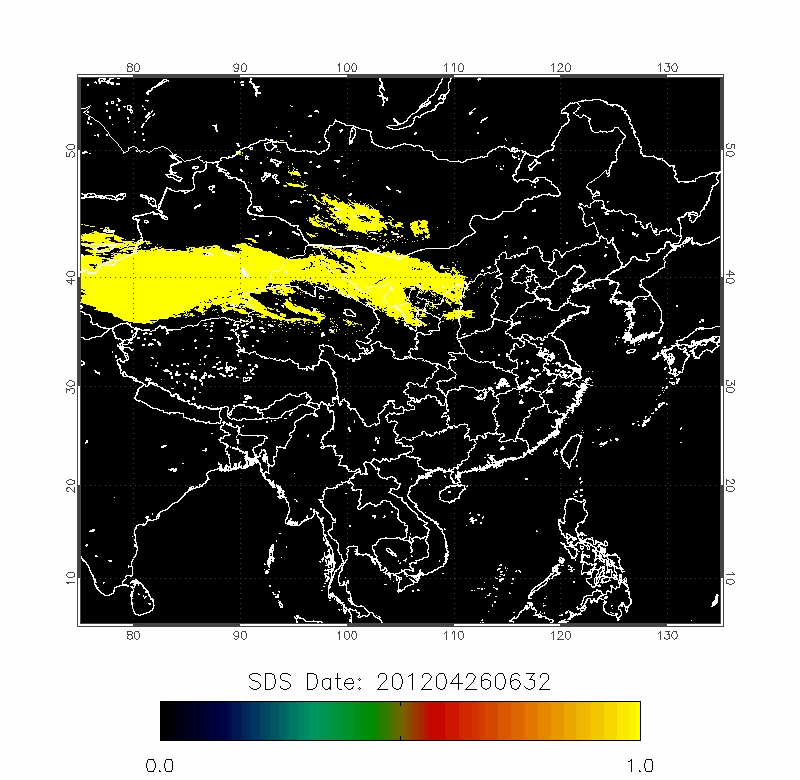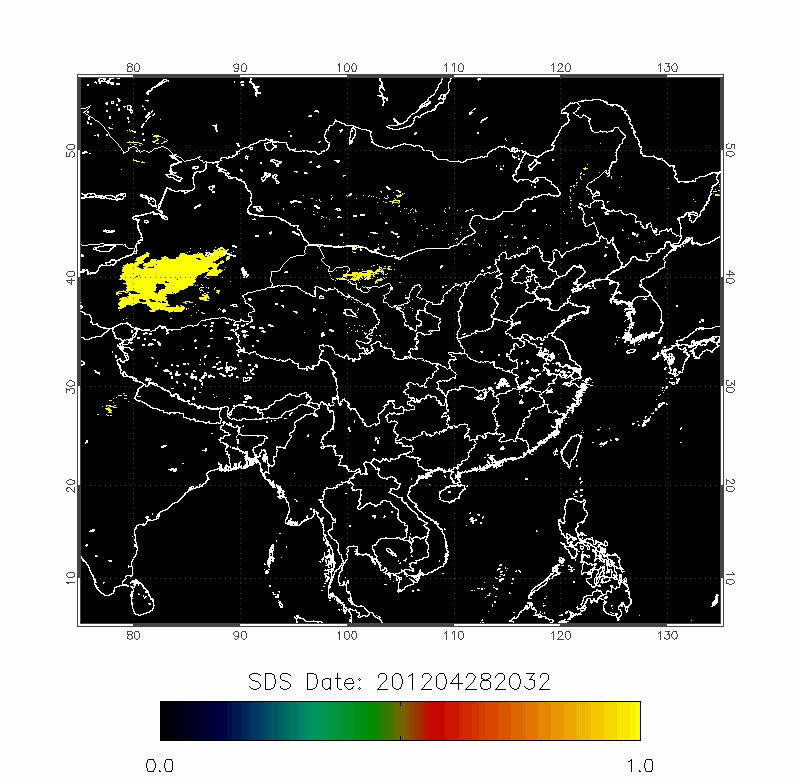
| 2010/03/18-2010/03/22 | 2012/04/18-2012/04/22 |
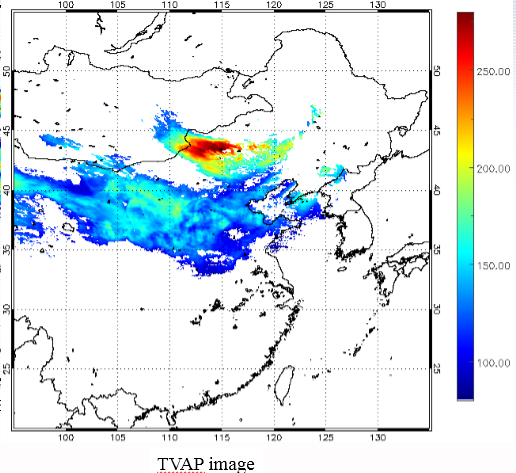
Ellrod et al. (2003) proposed another technique, the Three band Volcanic Ash Product (TVAP), for improved detection of volcanic ash, which utilizes BTD between three IR bands on GEOS satellite centered near 3.9, 10.7 and 12.0 µm.
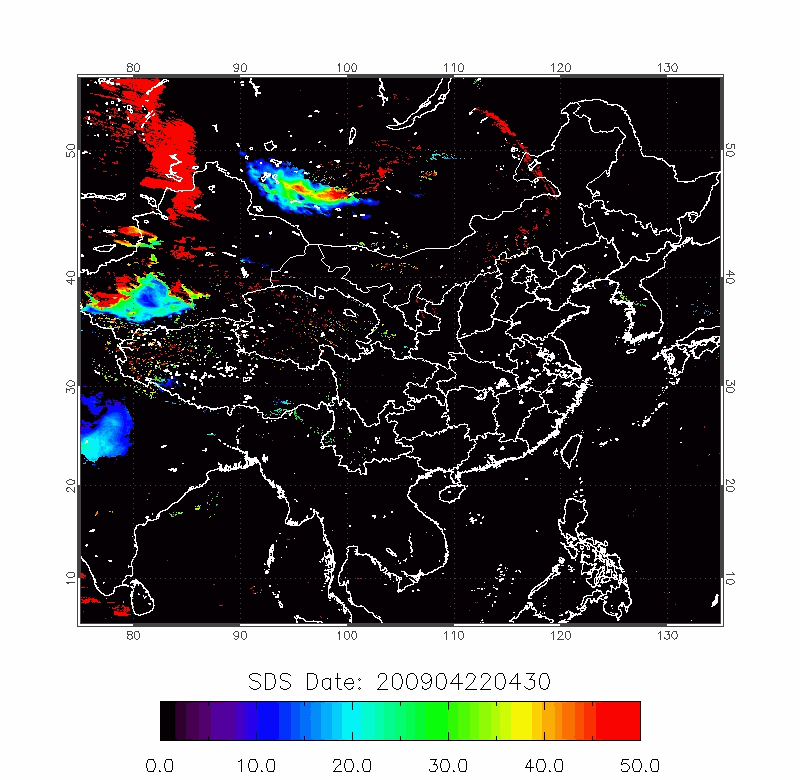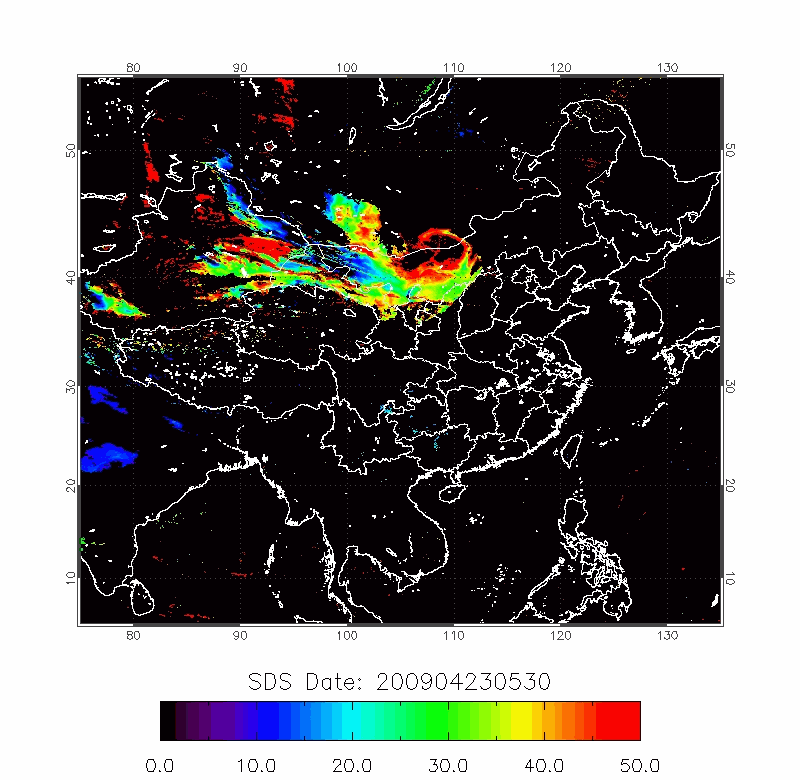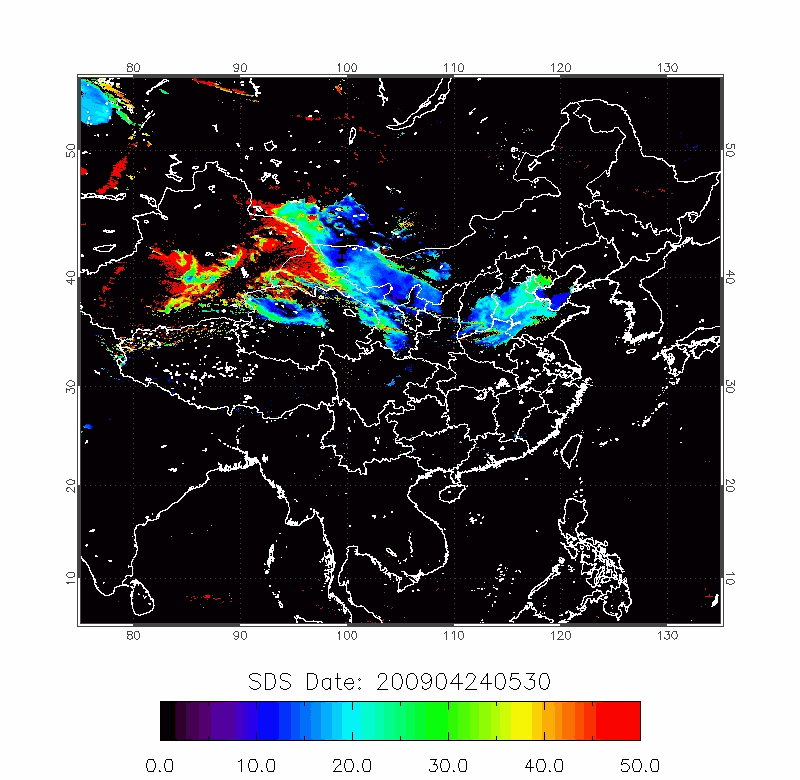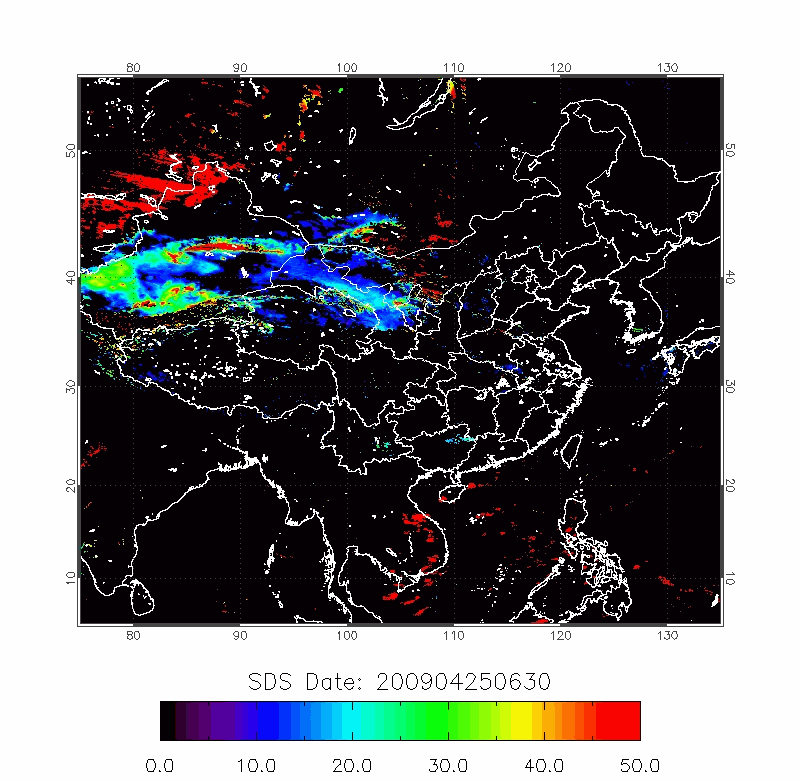
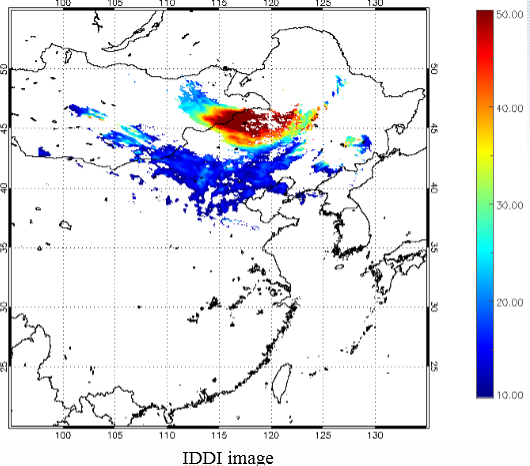
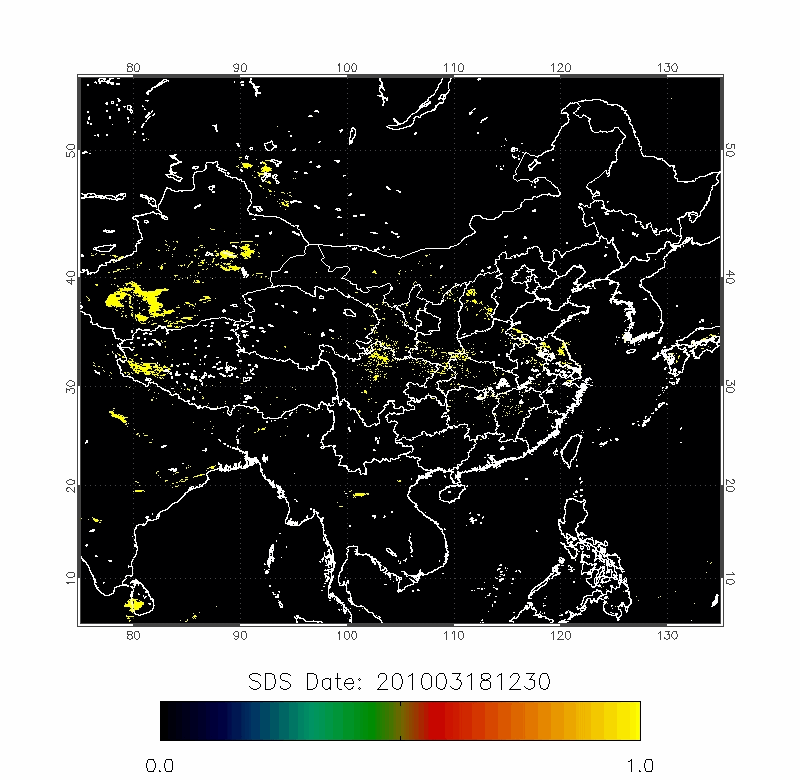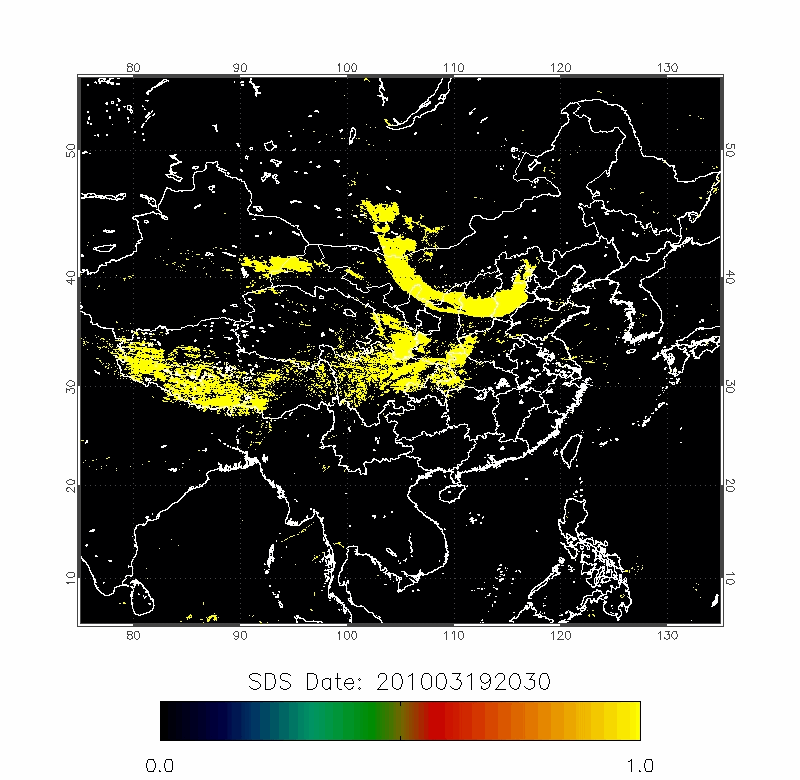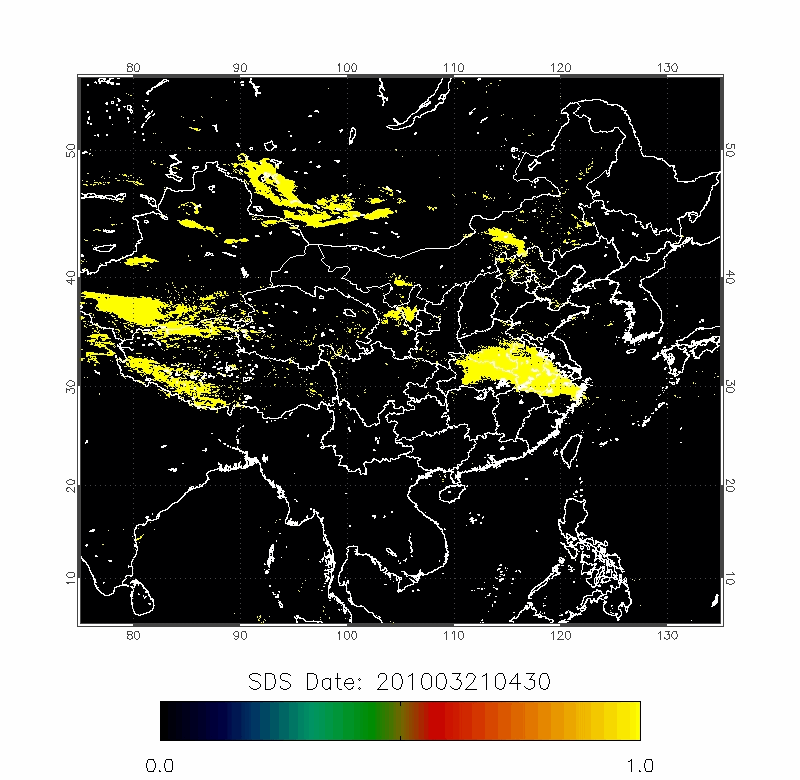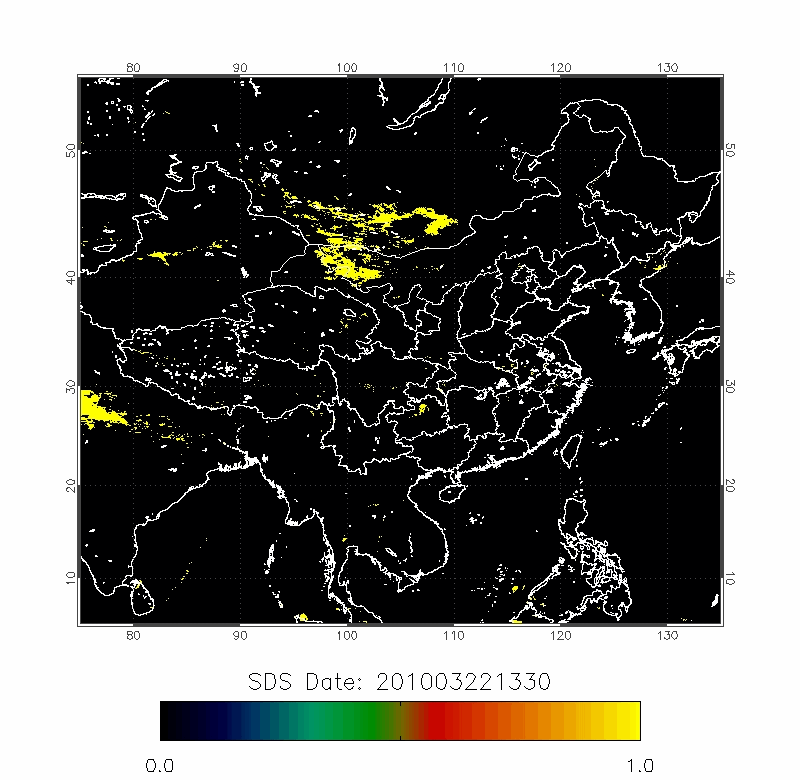
Legrand (2001) developed the Infrared Difference Dust Index (IDDI) to detect the presence of desert dusts over Africa. The rationale of IDDI is based on observing thermal radiation (10 µm -12 µm) emitted by the same scene over the course of several days, where distinct changes are evaluated for potential dust presence.
 |
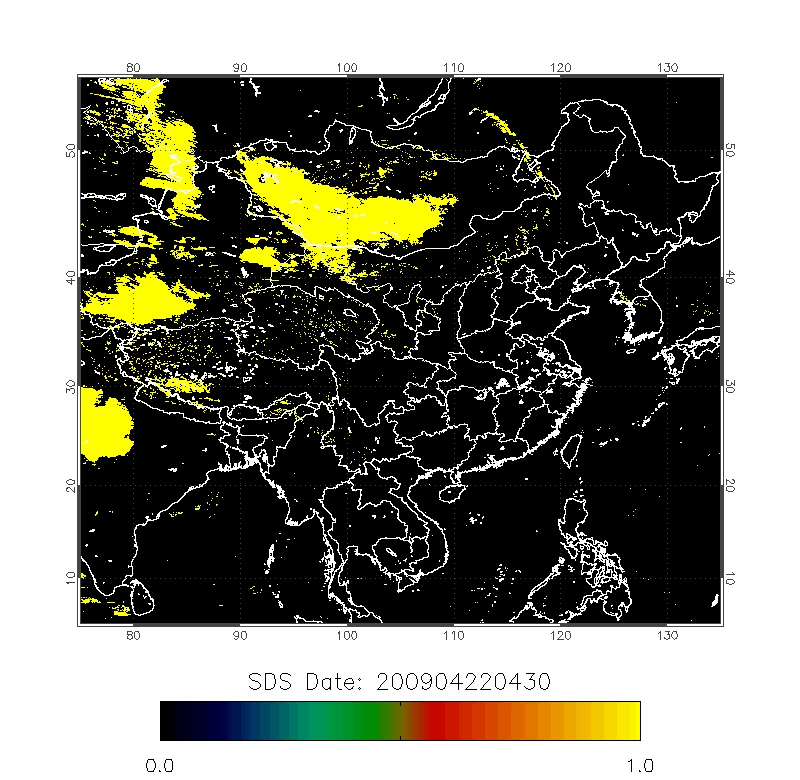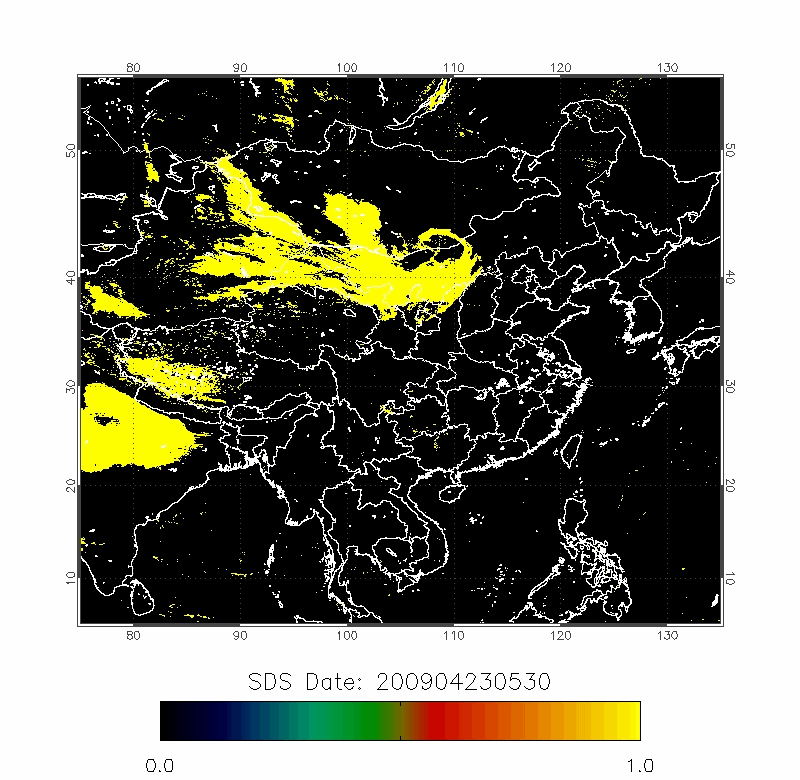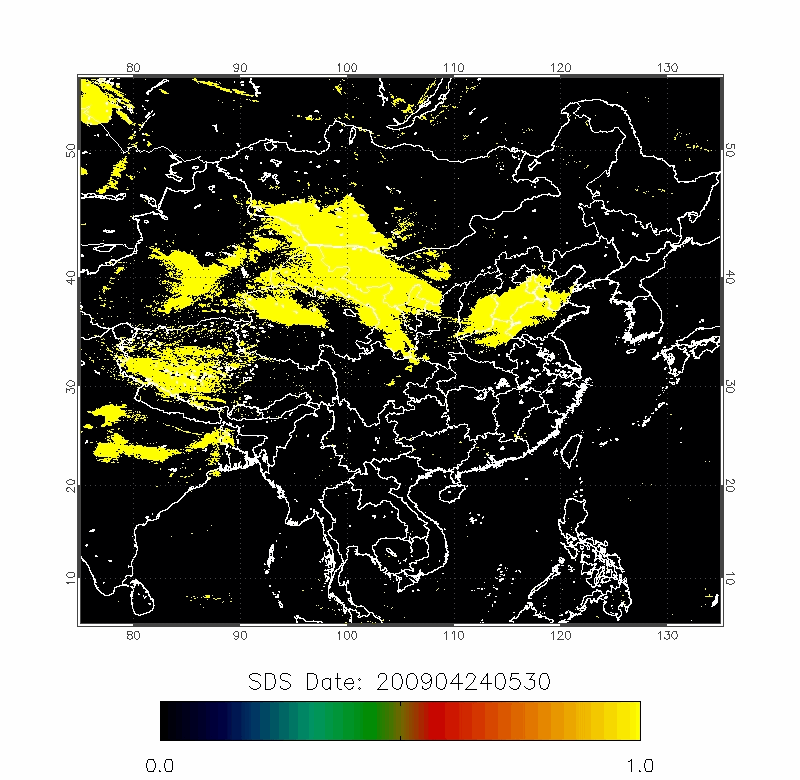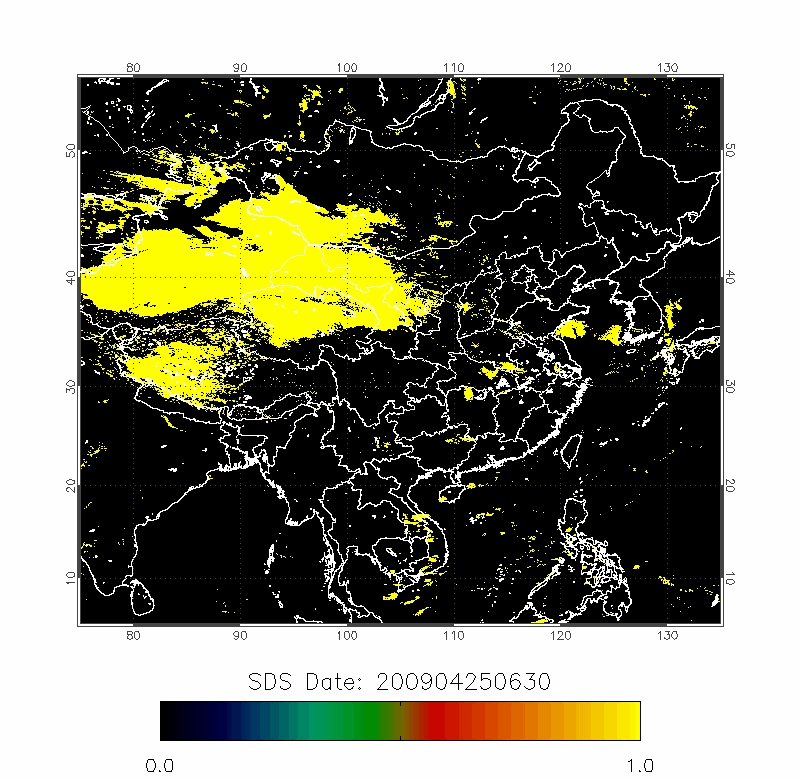 |
| IDDI Image | 2009/04/22-2009/04/25 |
 |
 |
| 2010/03/18-2010/03/22 | 2012/04/18-2012/04/22 |
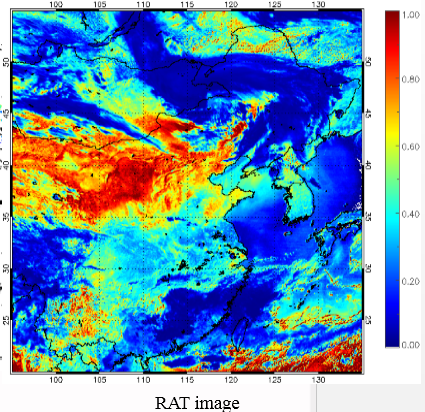
In the visible wavelengths, Pavolonis et al. (2006) analyzed the limitations of RAT and proposed another method that applies the ratio of reflectances at 3.75 µm and 0.65 µm (hereafter RAT (3.7 µm, 0.65µm)), as a complement for the automated detection of dust aerosols.
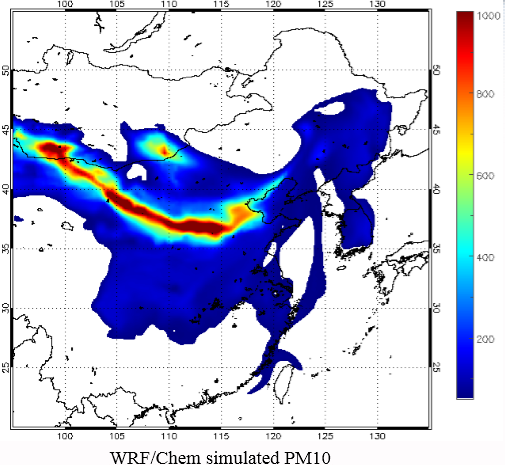
The WRF/Chem with inputs from the Goddard Chemistry Aerosol Radiation and Transport (GOCART) dust scheme are used to simulate dust storm outbreaks and transport processes in Asia. The WRF/Chem model is a fully-coupled meteorology-chemistry community model developed by NOAA together with partner research institutions (Bian, 2011). It is capable of simulating the chemistry of air pollutants, aerosols and dust storms, from local to global scales. For the dust model in WRF/Chem, there are five bins of dust mixing ratio (µg/kg) according to different effective radius, which are 0.5, 1.4, 2.4 4.5 and 8.0 µm respectively. The outputs of this study comprised simulated surface PM10 concentrations.
 |
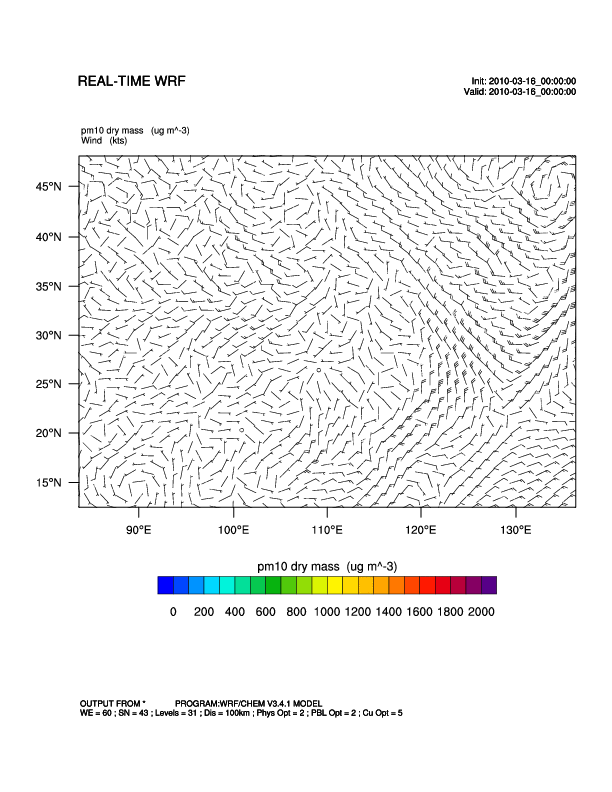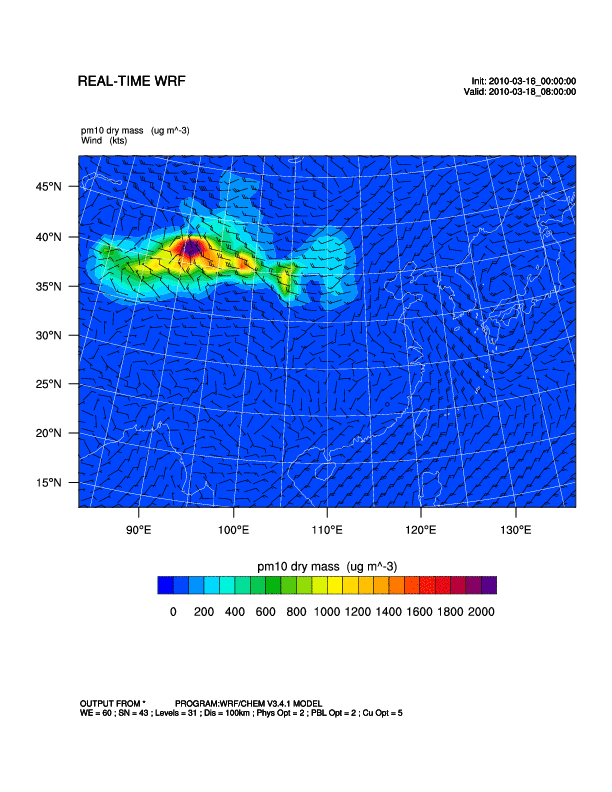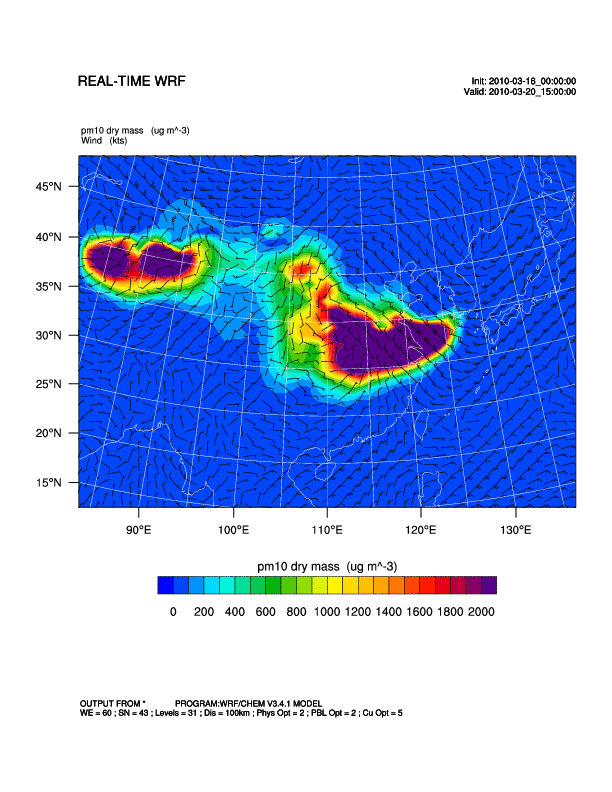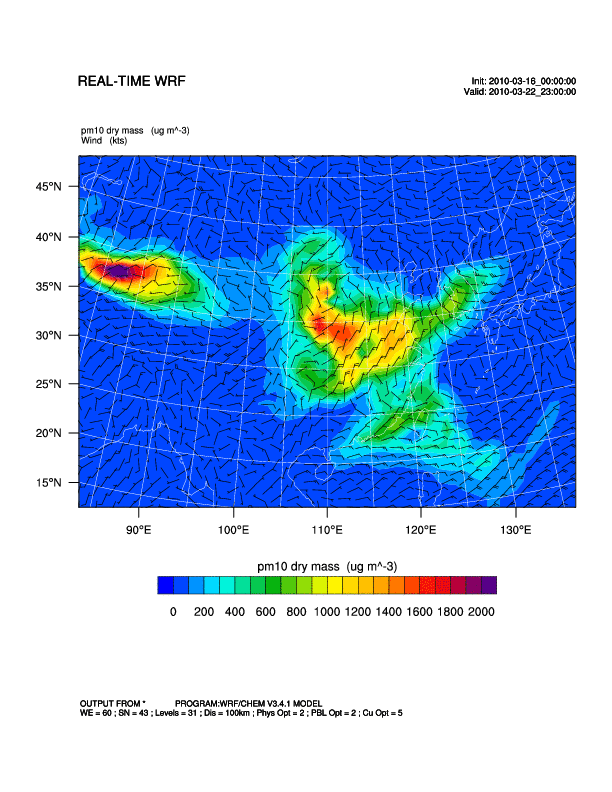 |
| WRF/Chem | 2010/03/16-2010/03/22 |
The Navy Aerosol Analysis Prediction System (NAAPS) model is developed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory for simulating dust and other pollutants dispersion.
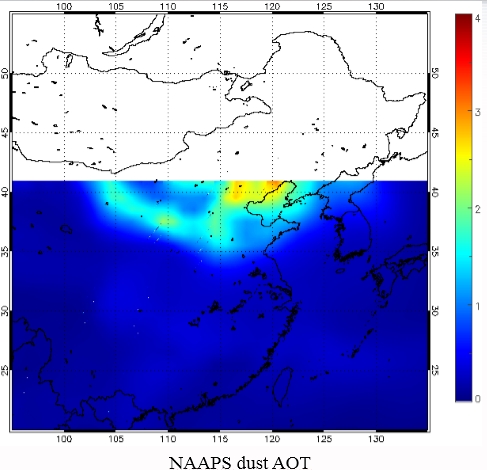 |
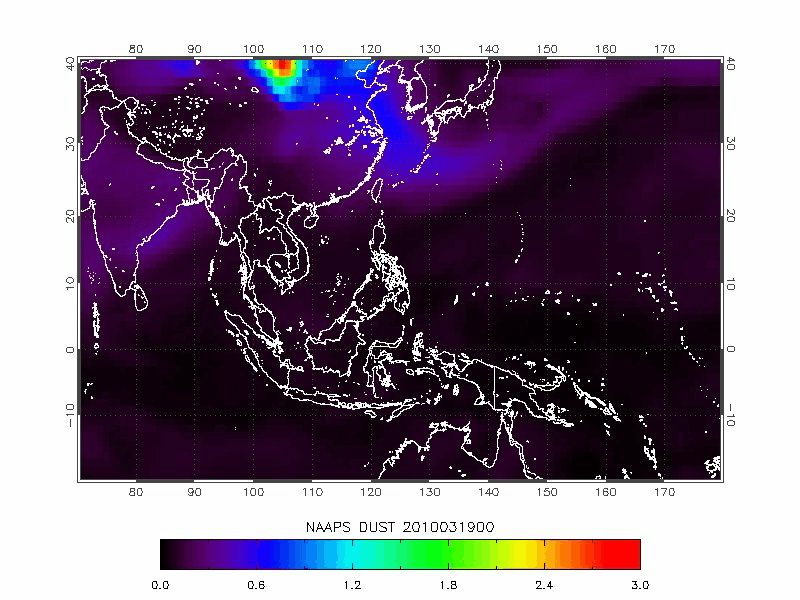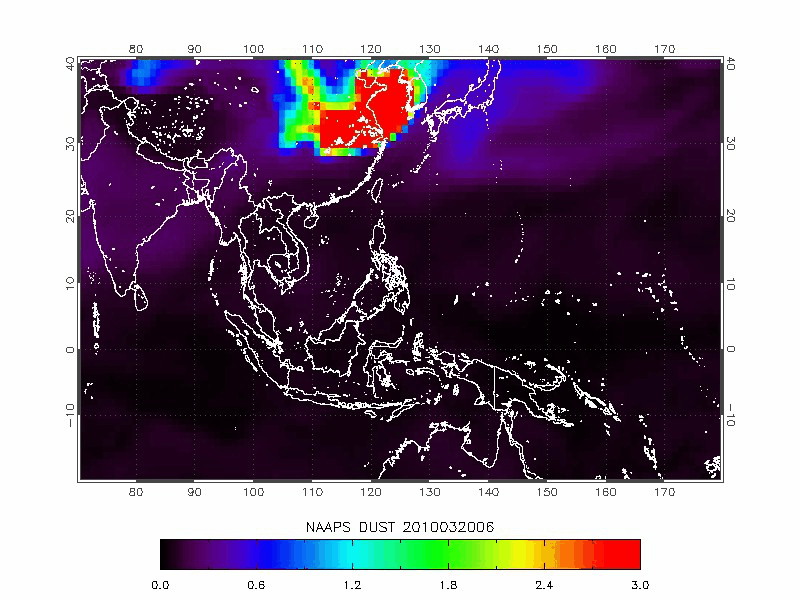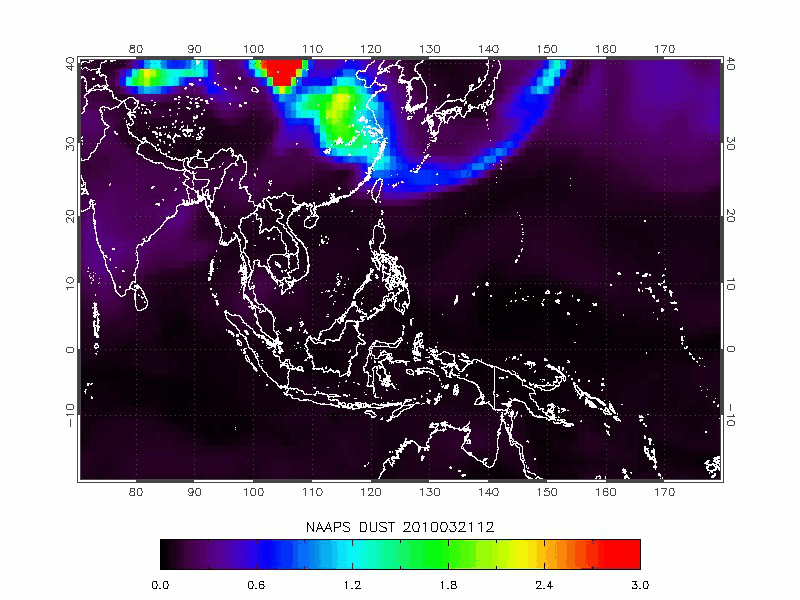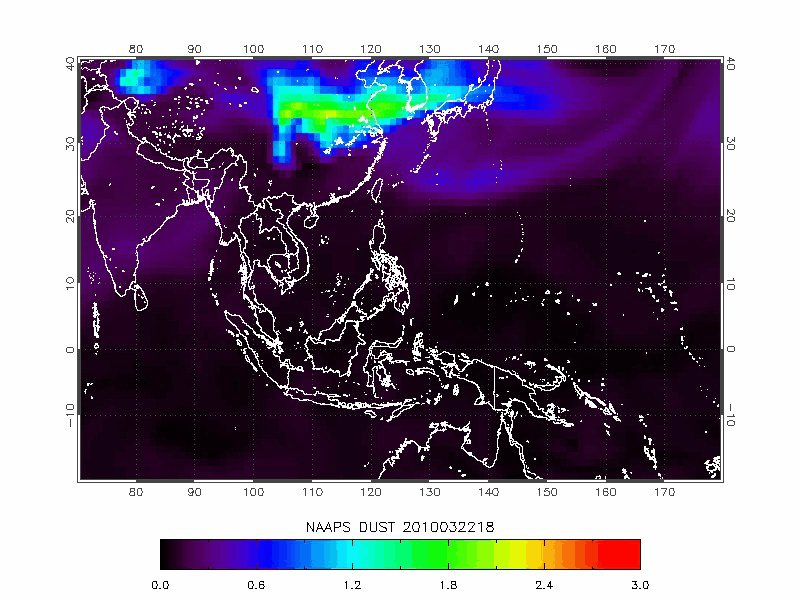 |
| Navy Aerosol Analysis Prediction System (NAAPS) | 2010/03/19-2010/03/22 |
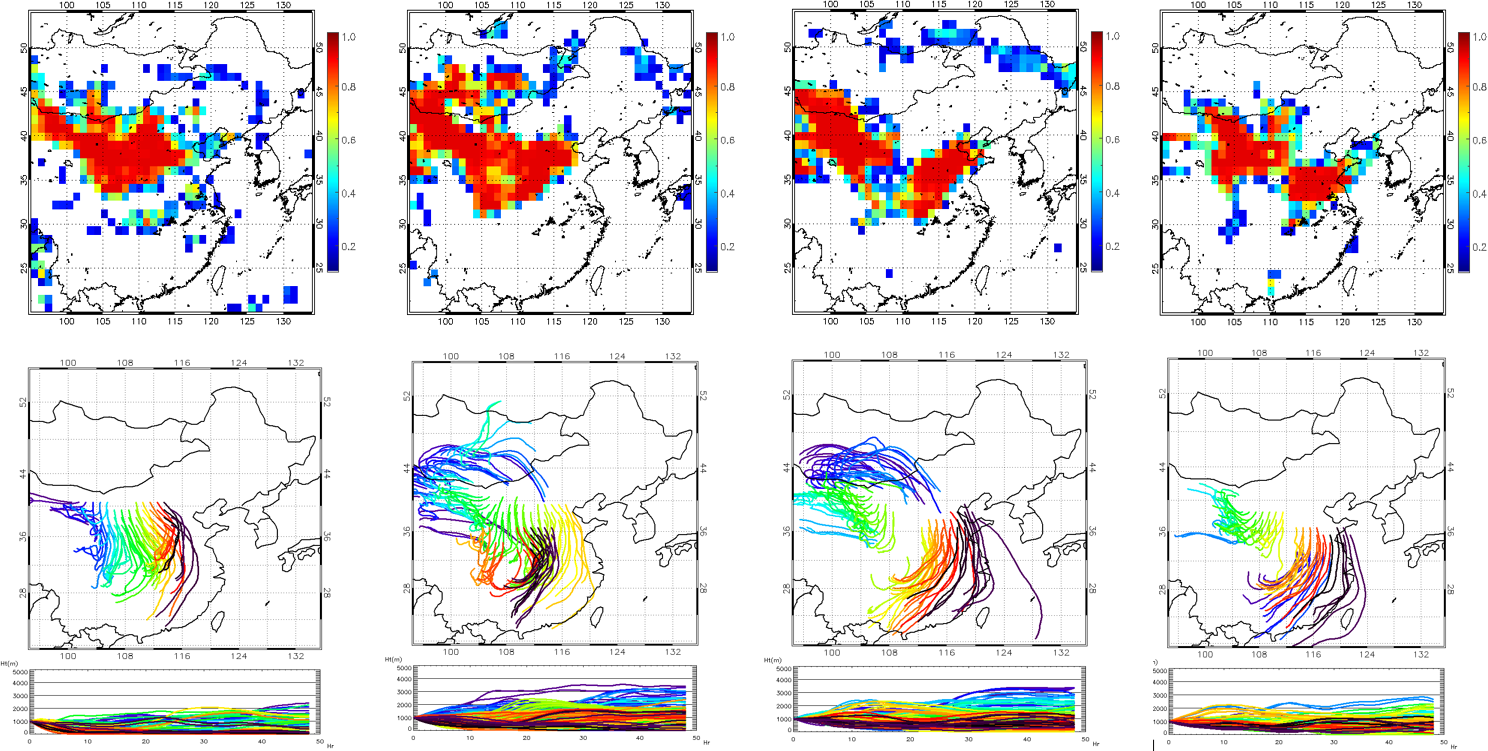
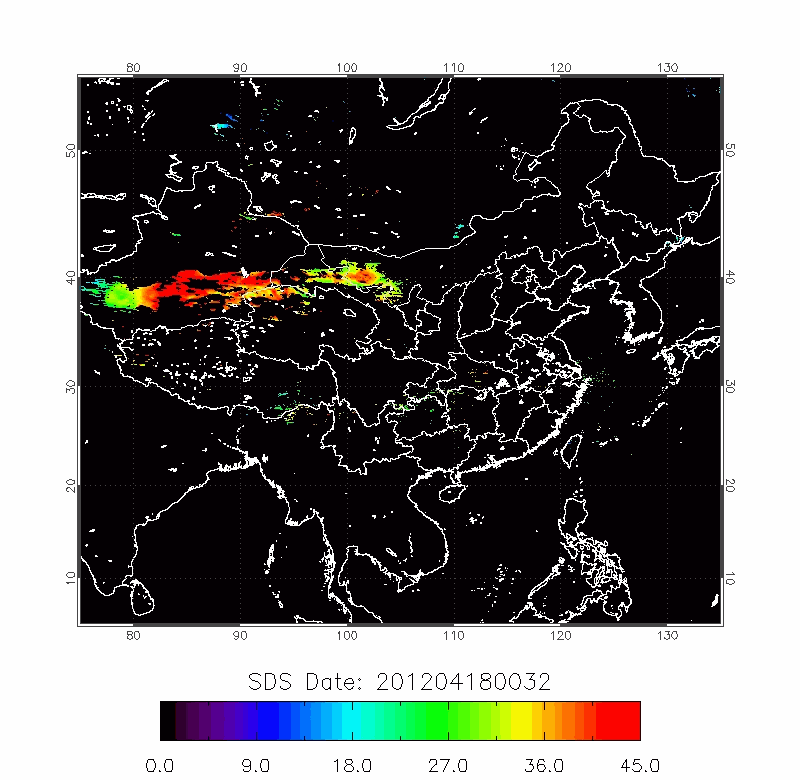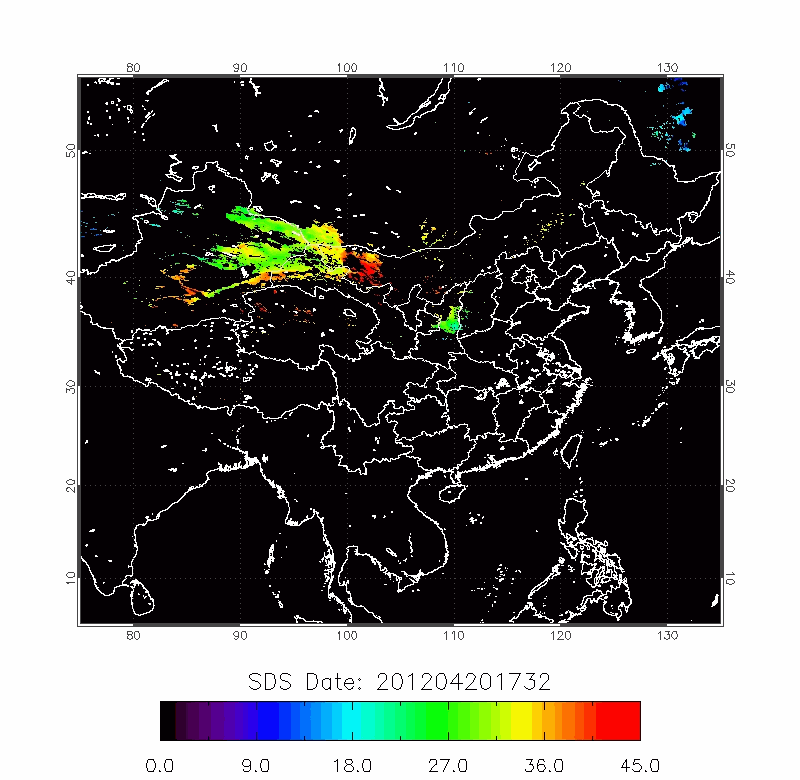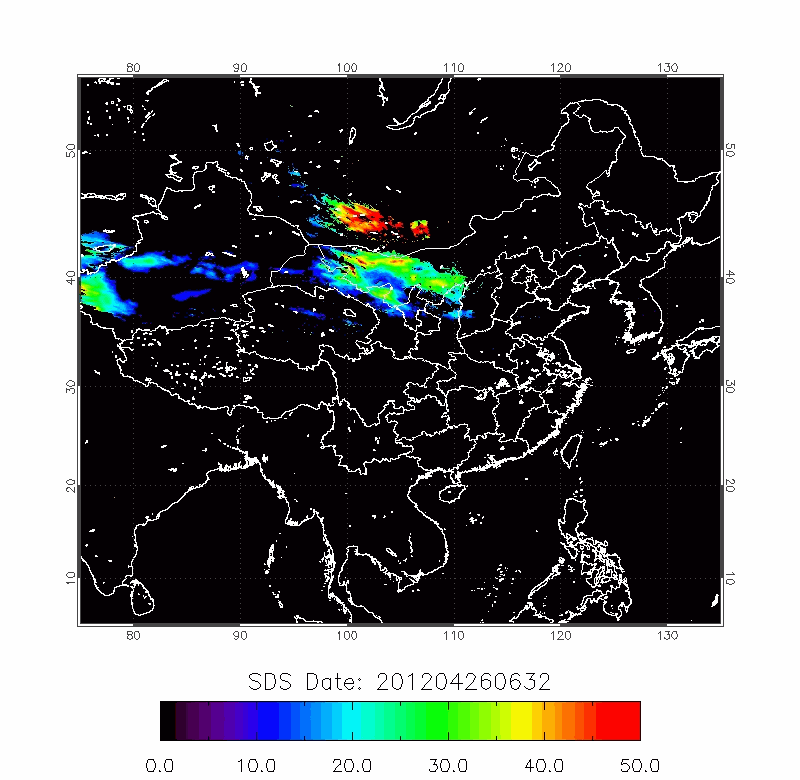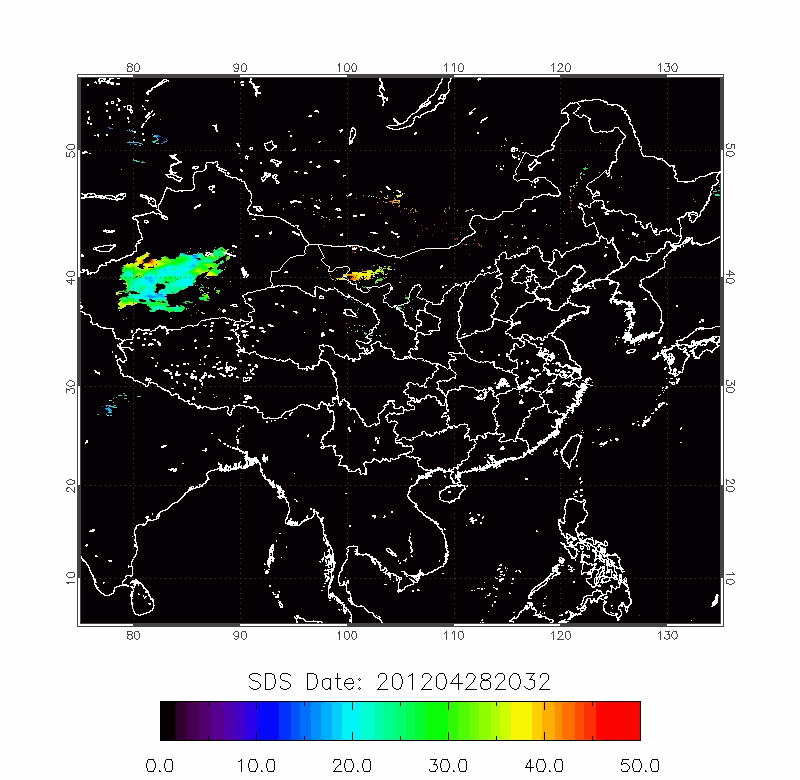
Upper row: A time series of posterior probabilities of dust storms using fast detection technique;
Lower row: The forward trajectories from the high posterior probabilities locations